Let's face it! Eating the best foods for Inflammatory Bowel Disease will not do you any good unless you sacrifice junk foods. In addition, frequent and unmonitored consumption of some hazardous foods triggers IBD flare-ups while weakening your immunity.
Therefore, you must let go of these harmful foods for the most effective results:
1. Dairy Products
If you are lactose intolerant, you must avoid all dairy products. Consuming them, even in the smallest quantity, can trigger inflammatory burning or redness reactions in the stomach or intestines.
You may choose soy, almond, or rice milk as alternatives to dairy products. However, you can consume dairy products in moderation if you have Inflammatory Bowel Disease when you are not experiencing its symptoms.
2. Highly Processed and Deep-Fried Foods
IBD patients must avoid frozen desserts, deep-fried snacks, packaged chips, packaged snacks and other processed food like burgers and pizza. These are usually cooked with plant fats or dalda, which do not digest quickly and worsen the stomach irritations of an IBD patient.
Secondly, fresh meat or vegetables are often not used to prepare processed foods like burgers. These can cause food poisoning and also trigger peptic ulcers.
If you consume them frequently, you can be easily prone to obesity, cardiac diseases, and even cancer.
3. Soda, Cold Drinks and Sugary Drinks
Cold drinks, soda, and other soft drinks have a high content of carbonated sugar and added flavours. These contain sweeteners like sorbitol, maltitol and xylitol, which are difficult for IBD patients to digest, causing bloating and diarrhoea.
If you notice the symptoms of Inflammatory Bowel Disease, lower your soda and cold drink consumption. Also, avoid soda and fruit juices from roadside stalls to stay safe from waterborne diseases.
4. Caffeinated and Alcoholic Beverages
Too much coffee, tea or alcohol can trigger peptic ulcers and symptoms of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Such drinks increase the motion of the GI tract, worsening the diarrhoea that comes with IBD. Therefore, you need to monitor your caffeine intake if you have IBD.
However, if coffee is your fuel to begin your day, go for different caffeinated substitutes that do not trigger IBD.
5. Hot and Spicy Food
Avoiding hot and spicy food is difficult when cooking Indian food. However, spicy foods are general triggers of inflammatory bowel disorder. As a result, most people complain of stomach and abdominal burns after a spicy meal.
Therefore, even if extreme spicy food attracts you, lower your intake of these food items while following an anti-inflammatory diet.
For people who do not have IBD, avoiding extreme spicy food from your diet is better to prevent such instances.
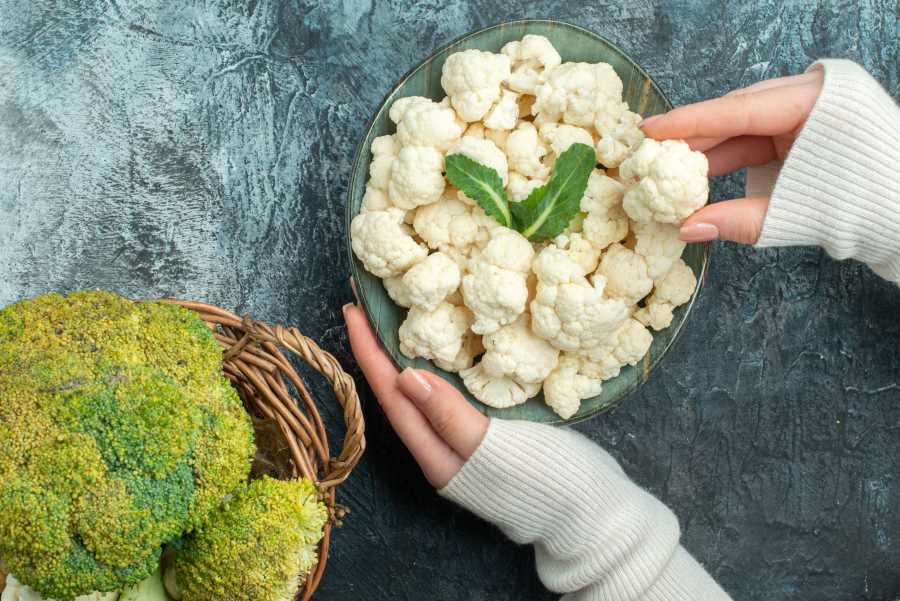
6. Raw Veggies of High-Fibre
Insoluble fibre is present in raw vegetables such as broccoli, cauliflower, and cabbage. This tends to be subpar for people who suffer from IBD. These foods can contribute to irritation in the gut lining, especially causing increased bloating, gas, and abdominal discomfort.
Cooking vegetables reduces the risks of triggering symptoms, as they are usually easy to tolerate when cooked. Tulsi oil helps fibre, which reduces fibre by boiling while retaining nutrients.
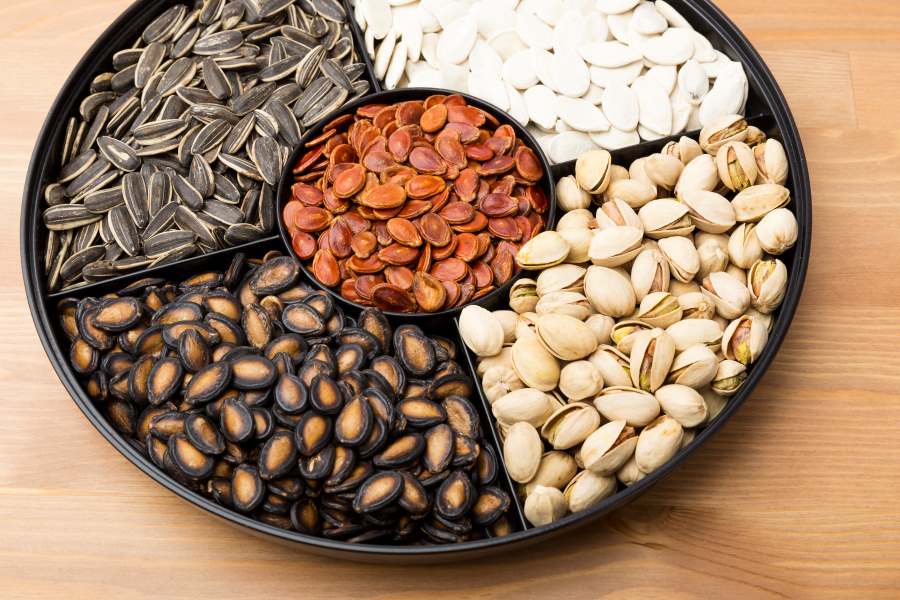
7. Nuts and Seeds
These foods, nuts and seeds, are hard to break and can also lead to inflammation of the digestive muscles. The hard coating of their seeds can aggravate flare-ups and the duration of the inflammation.
Since they are mostly not digested, they quickly pass through and can become a source of pain and discomfort. Smooth nut butter or butter without seeds is a good choice for active IBD symptoms.
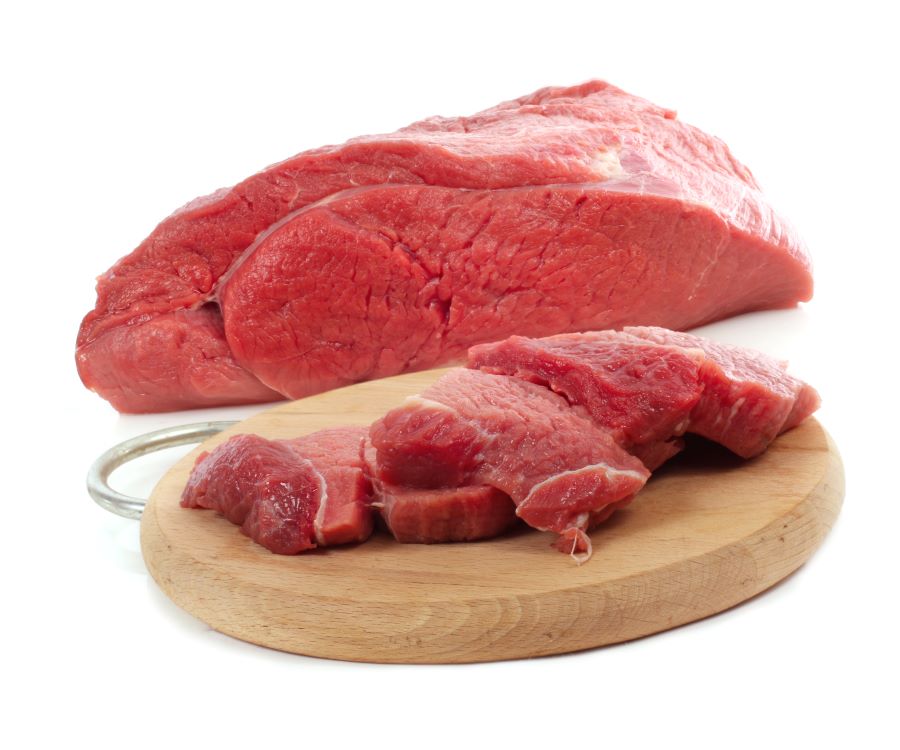
8. Red Meat and Fatty Cut's
Red meat and fatty cuts of pork or beef contain a high concentration of saturated fat, which aggravates intestinal inflammation. High-fat diets are tough for these individuals and probably the majority of people, so they likewise contribute to diarrhoea or pain in patients diagnosed with IBD.
Other protein options like fish and chicken and even plant sources will help preserve the proteins over the symptoms that calcium triggers.
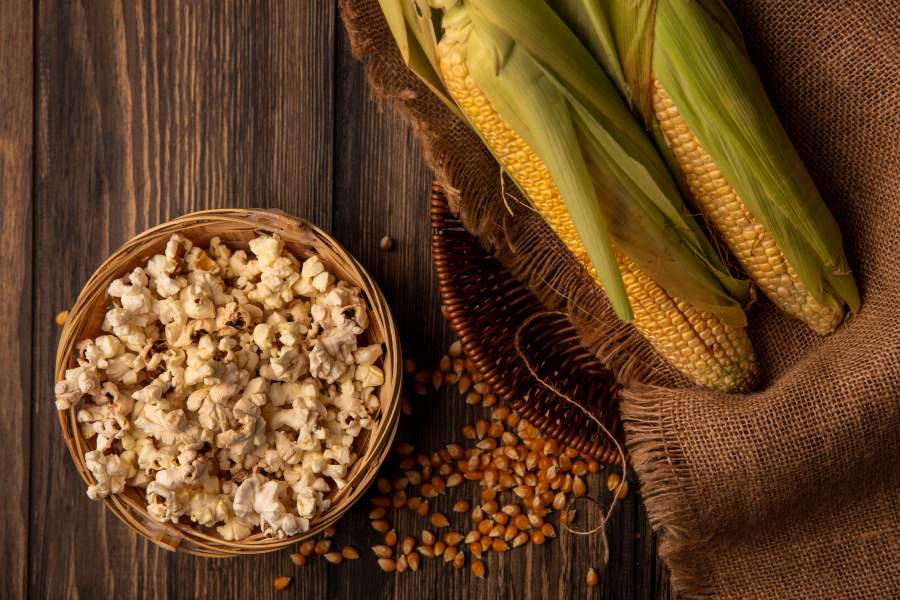
9. Corn and popcorn
Corn and popcorn are rich in insoluble fibres, making them very uncomfortable for binge eating and, among others, leading to bloating and pain in persons suffering from IBD. Their fibrous hulls are difficult to digest and thus can remain intact and passive in the intestines, causing erosion.
Corn-based and corn meal-containing dishes should be avoided regarding the chances of flare-ups.
10. Artificial Sweeteners
One example of artificial sweetener that is likely to be found in sugar-free products, especially chewing gums and coated candies, is sorbitol, which contains some reports of digestive discomfort such as vomiting, diarrhoea, smelly gas, and bloating. These additives cause disturbances in the gut flora, which may exacerbate bowel diseases.
However, these patients can handle safe sweeteners like honey or small portions of normal sugar instead of considering artificial sweeteners.