26 Best Foods for Diabetes for Faster Recovery
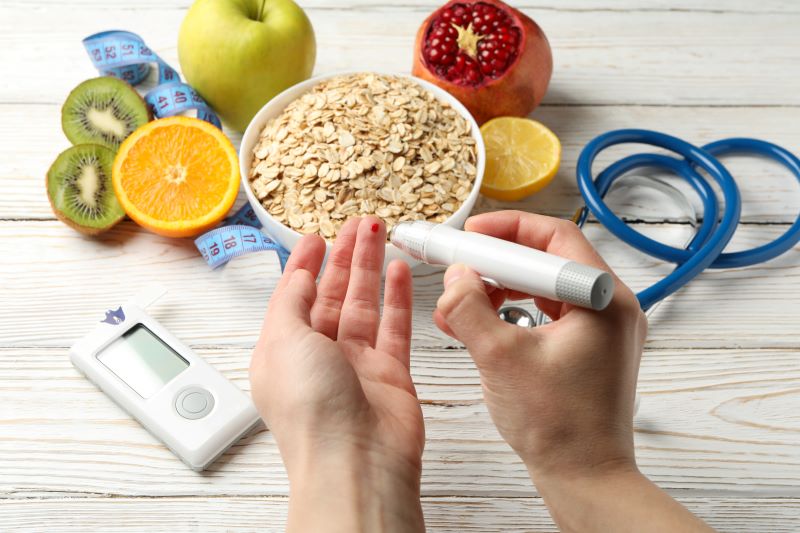

Eating the right diet is the key to faster healing and prolonging the quality of life for those with diabetes. Selective food combinations in your daily diet can dramatically affect sugar levels and enhance your health.
For faster diabetes recovery, certain foods can stabilise blood sugar levels effectively. These foods are rich in nutrients that support insulin sensitivity and management. Incorporating them into your diet can promote better glucose control and overall health.

Table of Contents

What is Sugar/Diabetes?
Sugar is a type of carbohydrate that provides energy to the body. Excess sugar consumption can lead to health issues like diabetes. Diabetes is a condition where blood sugar levels are chronically elevated. There are two main types: type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes occurs when the pancreas doesn't produce enough insulin. Type 2 diabetes happens when the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn't produce enough. Proper management involves maintaining a balanced diet and regular exercise.
26 Best Foods for Diabetes
A variety of foods can help manage blood sugar levels effectively. These foods are low in refined sugars and carbohydrates, preventing spikes in blood glucose. Incorporating them into your diet can improve insulin sensitivity and glycemic control.
Foods rich in fibre slow down digestion, preventing rapid blood sugar fluctuations. Healthy fats and lean proteins promote satiety and stabilise blood sugar levels. Including these diabetes-friendly foods in your meals can support overall health.
Nevertheless, here are some food suggestions to add to the diet for Sugar/ Diabetes and their nutritional values:
List of Fibre-Rich Vegetables for Diabetes
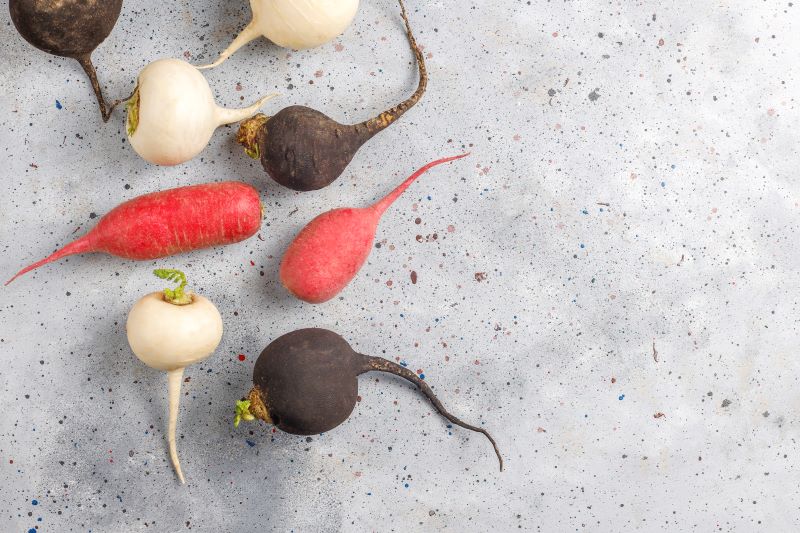

Fibre-rich vegetables are essential for managing diabetes and promoting overall health. These vegetables help regulate blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity effectively. Including a variety of them in your diet can support diabetes management.
SNo. |
Vegetables | Description | Amount of Fibre (per 100 g) |
| 1 | Kohlrabi | Kohlrabi is a cruciferous vegetable rich in fibre, vitamin C, potassium, and antioxidants. | 3.6 g |
| 2 | Jicama | Jicama is a crisp, sweet root vegetable packed with fibre, vitamin C, potassium, and prebiotics. | 4.9 g |
| 3 | Radish | Daikon radish is low in calories and high in fibre, vitamin C, potassium, and antioxidants. | 1.6 g |
| 4 | Chinese Okra | Chinese okra, or luffa, is a fibrous vegetable rich in fibre, vitamin C, potassium, and calcium. | 0.5 g |
| 5 | Yardlong Bean | Yardlong beans are elongated pods with fibre, vitamin C, folate, potassium, and iron. | 3.4 g |
List of Fruits and Juices for Diabetes
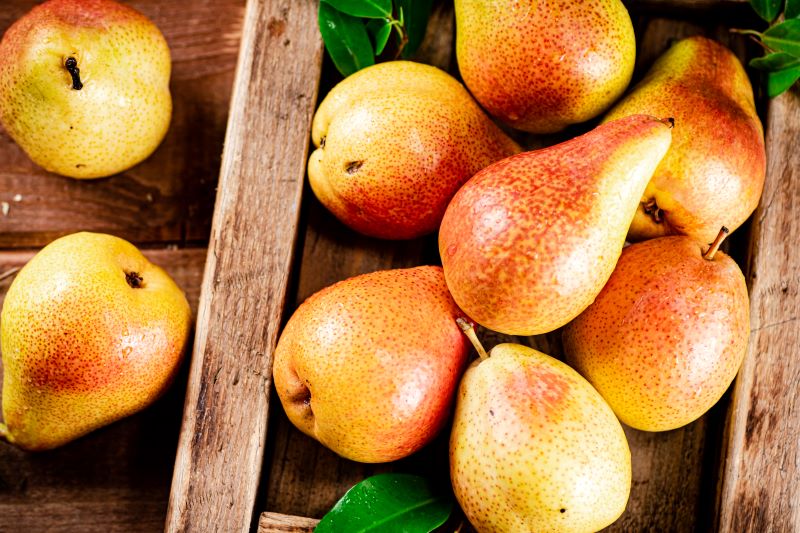

Fibre-rich fruits and juices are beneficial for managing diabetes effectively. They help regulate blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity naturally. Incorporating these into your diet can support overall diabetes management.
SNo. |
Fruits and Juices | Description | Amount of Fibre (per 100 g) |
| 6 | Raspberries | Bursting with antioxidants, raspberries provide fibre, vitamin C, and manganese. They also offer phytonutrients like ellagic acid, which may help lower the risk of chronic diseases. | 6.5 g |
| 7 | Blueberries | Blueberries are rich in fibre, heart-healthy fats, potassium, and vitamin E. Its fibre content supports digestion and helps regulate blood sugar levels. | 8.7 g |
| 8 | Prunes (Juice) | Prune juice, derived from dried plums, is rich in fibre, particularly soluble fibre, which promotes digestive health and helps regulate blood sugar levels. It's also a source of vitamins and minerals. | 2.6 g |
| 9 | Pears | Sweet and succulent, Pears provide good fibre, vitamin K, and copper sources, supporting bone health and immune function. Their soluble fibre aids in maintaining steady blood sugar levels. | 3.1 g |
| 10 | Guava Juice | Guava juice offers a tropical twist with its high fibre content, vitamin C and antioxidants. | 0.6 g |
| Promoting digestive health and boosting immunity. It's a refreshing choice for hydration and blood sugar control. | |||
| 11 | Pineapple Juice | Pineapple juice is delicious and rich in fibre, vitamin C, and bromelain, supporting digestion and reducing inflammation. Its fibre content helps slow down sugar. Absorption aids in Blood sugar management. | 0.2 g |
List of Dairy Products and Nuts for Diabetes
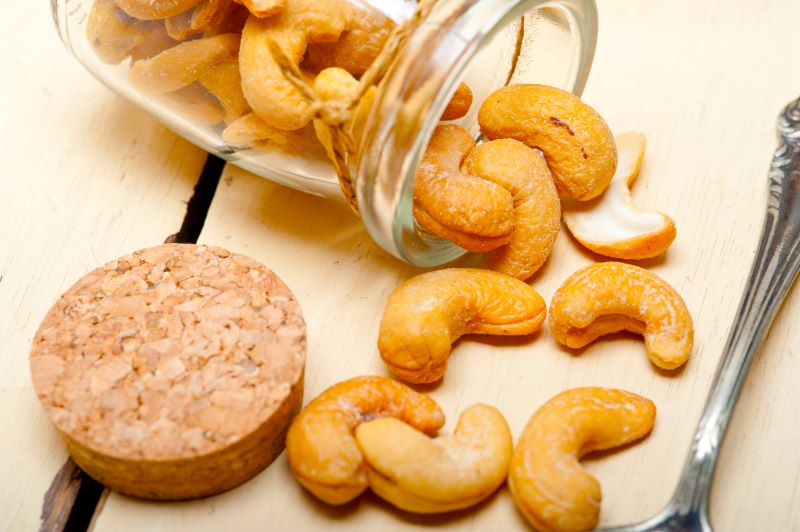

Numerous dairy products and nuts are fibre-rich and beneficial for diabetes management. Fibre helps regulate blood sugar levels, improving insulin sensitivity and reducing spikes:
SNo. |
Dairy Products and Nuts | Description | Amount of Fibre (per 100 g) |
| 12 | Cottage Cheese | Cottage cheese is a low-fat dairy product rich in protein, calcium, and phosphorus. It also provides vitamins B12 and riboflavin. | 0.4 g |
| 13 | Cashews | Cashews are nutrient-dense nuts packed with protein, healthy fats, and minerals like magnesium and zinc. They also contain vitamins E, K, and B6. | 3.3 g |
| 14 | Pistachios | Pistachios are a source of protein, healthy fats, and antioxidants like lutein and zeaxanthin. They also offer vitamins B6 and K, along with potassium and phosphorus. | 10.3 g |
| 15 | Walnuts | Walnuts are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which promote heart health. They also provide protein, fibre, vitamins E and B6, magnesium, and phosphorus. | 6.7 g |
| 16 | Hazelnuts | Hazelnuts contain healthy fats, protein, and antioxidants like vitamin E and manganese. They also offer folate, potassium, and magnesium. | 13.6 g |
List of Fibre-Rich Vegetarian Food for Diabetes

A range of fibre-rich vegetarian foods can benefit individuals managing diabetes. These foods help stabilise blood sugar levels and improve overall glycemic control. Incorporating them into your diet can promote better long-term health outcomes.
SNo. |
Food | Description | Amount of Fibre (per 100 g) |
| 17 | Fenugreek | Fenugreek, or Methi, is a popular spice and herb known for its bitter taste and medicinal properties. It's rich in soluble fibre, protein, iron, magnesium, and manganese. | 24.6 g |
| 18 | Oats | Oats are versatile whole grains rich in soluble fibre, beta-glucans, protein, iron, magnesium, and zinc. They help stabilise blood sugar levels and promote heart health. | 10.6 g |
| 19 | Bananas | Bananas are a delicious and convenient source of fibre, potassium, vitamin C, vitamin B6, and antioxidants. They provide sustained energy and aid digestion. | 2.6 g |
| 20 | Sweet Potato | Sweet potatoes are nutrient-dense root vegetables packed with fibre, vitamins A and C, potassium, and antioxidants. They have a lower glycemic index compared to regular potatoes. | 3.3 g |
| 21 | Kale | Kale is a leafy green vegetable loaded with fibre, vitamins A, C, and K, calcium, iron, and antioxidants. It supports digestive health, boosts immunity, and aids in blood sugar control. | 2 g |
List of Non-Vegetarian Food for Diabetes
For individuals managing diabetes, incorporating protein-rich, non-vegetarian foods into their diet is crucial. These options offer essential nutrients while helping to regulate blood sugar levels. Here's a selection of such foods:
SNo. |
Food | Description | Amount of Protein (per 100 g) |
| 22 | Eggs | Eggs are a complete protein source rich in essential amino acids, vitamins (A, D, B12), and minerals (iron, zinc). They provide satiety and support muscle health. | 20 g |
| 23 | Fish | Fish, such as salmon or mackerel, is abundant in omega-3 fatty acids, protein, and vitamin D. It promotes heart health and reduces inflammation. | 34 g |
| 24 | Chicken | Chicken is a lean protein source with nutrients like niacin, phosphorus, and selenium. It supports muscle growth and repair. | 35 g |
| 25 | Meat | Like beef or lamb, meat is rich in protein, iron, and zinc. It provides essential amino acids necessary for muscle health and overall body function. | 25 g |
| 26 | Shrimp | Shrimp is low in fat and calories but high in protein, vitamin B12, and selenium. It supports muscle health and provides important minerals for metabolism. | 30 g |
Causes of Sugar/Diabetes
Discovering the reasons for the diagnosis can greatly help in the prevention strategies and treatment. Genetic and family history contribute a lot to its development. However consistent, lifestyle factors must be carefully addressed, too.
- Genetic Predisposition: Genetic predisposition influences susceptibility to certain health conditions and traits.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Inactivity promotes insulin resistance, and cellular systems thus cannot optimally utilise glucose.
- Poor Diet: Consuming large amounts of sugary foods, refined carbohydrates, and unhealthy fats results in excess weight.
- Obesity: Becoming overweight or obese substantially lowers the likelihood of experiencing type 2 diabetes.
- Insulin Resistance: Insulin resistance occurs when cells cannot respond to insulin well.
Symptoms of Sugar/Diabetes
Symptoms of diabetes include increased thirst, frequent urination, and unexplained weight loss. Fatigue, blurred vision, and slow wound healing are also common indicators. If experiencing these symptoms, it's crucial to consult a healthcare professional.
- Increased Thirst and Urination: These are the common symptoms of uncontrolled diabetes mellitus. Excess glucose in the bloodstream triggers the body to expel it through urine.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Unexplained weight loss can be a symptom of undiagnosed diabetes. High blood sugar levels cause excessive urination and calorie loss.
- Fatigue: Tiredness and fatigue can result from disrupted normal energy production, when cells do not receive enough glucose due to high blood sugar levels.
- Blurred Vision: Blurred vision is a common symptom of diabetes-related eye problems. High blood sugar levels can cause swelling in the eye's lenses.
- Slow Healing Wounds: Recognising symptoms early can help manage sugar levels and prevent complications. Regular monitoring and lifestyle changes are crucial for managing diabetes effectively.
Recognising symptoms early can help manage sugar levels and prevent complications. Regular monitoring and lifestyle changes are crucial for managing diabetes effectively. Consulting a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment is essential.
How to Maintain a Healthy Diet for Diabetes?
Maintaining a healthy diet is crucial for managing diabetes and ensuring overall well-being. Here's how to do it effectively:
- Focus on Balanced Meals: A balanced plate with carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats. Incorporate plenty of non-starchy vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Monitor Carbohydrate Intake: Be mindful of carbohydrate intake, as they directly impact blood sugar levels. Opt for complex carbohydrates with fibre, such as whole grains, legumes, and vegetables.
- Portion Control: Pay attention to portion sizes to avoid overeating, which can lead to spikes in blood sugar levels. Use smaller plates, and practice mindful eating to prevent unnecessary calorie consumption.
- Choose Low-Glycemic Index Foods: Select foods with a low glycemic index (GI), which are digested more slowly. These include whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes.
- Stay Hydrated and Limit Sugary Drinks: Opt for water or other non-caloric beverages instead of sugary drinks like soda or fruit juice, which can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels.
Maintaining a healthy diet for diabetes involves focusing on balanced meals, monitoring carbohydrate intake, practising portion control, choosing low-GI foods, and staying hydrated while limiting sugary drinks. By making informed food choices and being mindful of portion sizes, individuals with diabetes can better manage their condition and improve their overall quality of life.
10 Food Items to Avoid When Suffering from Diabetes
When managing diabetes, it's crucial to be mindful of dietary choices to maintain stable blood sugar levels. Certain foods can significantly impact glucose levels and should be limited or avoided altogether. Here are ten food items to steer clear of when dealing with diabetes
SNo. |
Food Item | Reasons to Avoid |
| 1 | Sugary Beverages | Spike blood sugar levels rapidly. |
| 2 | White Bread and Pasta | High glycemic index, leading to blood sugar spikes. |
| 3 | Processed Snacks | Loaded with unhealthy fats and refined carbohydrates. |
| 4 | Sugary Desserts | Contribute to sharp increases in blood glucose. |
| 5 | Sweetened Breakfast Cereals | Contains added sugars and lacks fibre. |
| 6 | Fried Foods | High in unhealthy fats, promoting insulin resistance. |
| 7 | Fruit Juices | Concentrated sugars, lacking fibre found in whole fruits. |
| 8 | Flavored Yogurt | Often contain added sugars, affecting blood sugar control. |
| 9 | Packaged Baked Goods | High in refined flour and sugars, disrupting blood sugar. |
| 10 | Alcohol | It can cause fluctuations in blood sugar levels and impair judgment. |
Incorporating a balanced diet low in sugar and unhealthy fats while prioritising whole, unprocessed foods can help manage diabetes effectively.
Side Effects of an Unhealthy Diet for Diabetes
An unhealthy diet for diabetes can exacerbate symptoms and complications significantly. High blood sugar levels can lead to fatigue, nerve damage, and infections. Additionally, poor dietary choices can contribute to weight gain and cardiovascular issues.













