9000+ Cashless
Network Garages
96% Claim
Settlement (FY23-24)
24*7 Claims
Support
Click here for new car
I agree to the Terms & Conditions

General
General Products
Simple & Transparent! Policies that match all your insurance needs.


37K+ Reviews
7K+ Reviews
Scan to download
Life
Life Products
Digit Life is here! To help you save & secure your loved ones' future in the most simplified way.


37K+ Reviews
7K+ Reviews
Scan to download
Claims
Claims
We'll be there! Whenever and however you'll need us.


37K+ Reviews
7K+ Reviews
Scan to download
Resources
Resources
All the more reasons to feel the Digit simplicity in your life!
 Tools & Calculators
Tools & Calculators


37K+ Reviews
7K+ Reviews
Scan to download
37K+ Reviews
7K+ Reviews
 Logout
Logout
Our WhatsApp number cannot be used for calls. This is a chat only number.


9000+ Cashless
Network Garages
96% Claim
Settlement (FY23-24)
24*7 Claims
Support
Click here for new car
I agree to the Terms & Conditions

Add Mobile Number
Sorry!

9000+ Cashless
Network Garages
96% Claim
Settlement (FY23-24)
24*7 Claims
Support
Terms and conditions
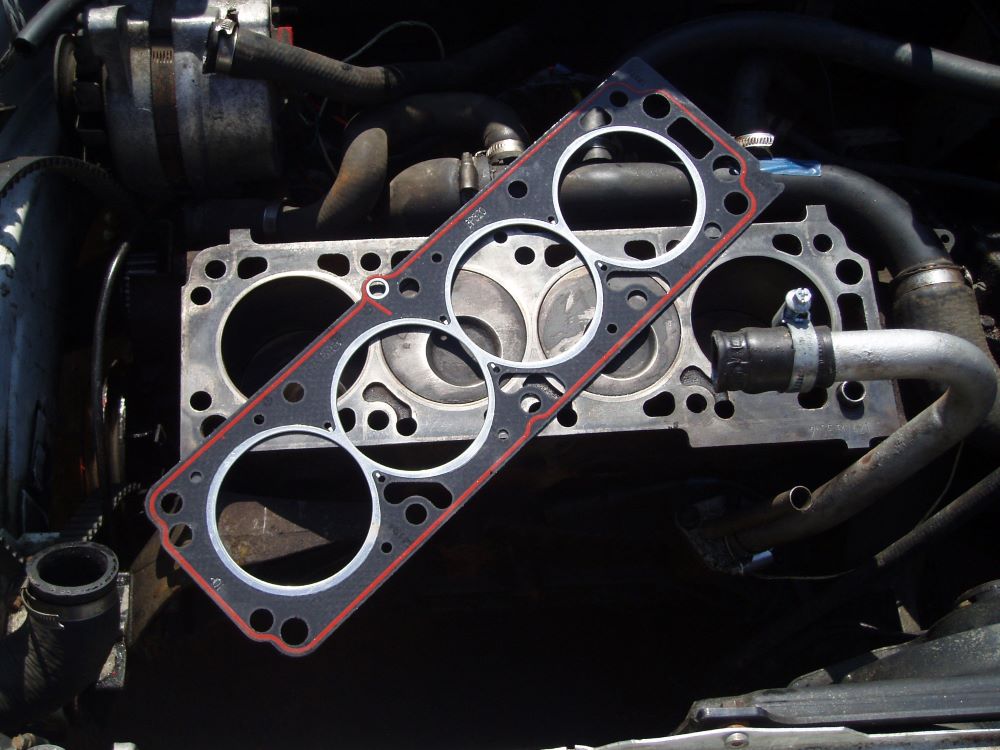
Car is a reflection of fine engineering. Propelled by a combustion engine, it is an assemblage of several elements. Among them, a head gasket holds a major significance. This small yet crucial element is fitted between the engine block and cylinder head.
The primary purpose of it is to fasten the inner combustion process allowing oil and refrigerant to flow freely to lubricate and cool down the engine.
Head gaskets are multi-layered machine-casted components manufactured specifically for inner combustion engines. They come with tubular bored holes for hosting pistons. It maintains an optimum compression ratio across the chamber, allowing your car's engine to perform flawlessly.
Though usually a gasket is made of a composition of steel and elastomer, it can also be developed using copper, silicone, or rubber.
Most vehicles' engines comprise two parts: an engine block and a cylinder head dashed on top. While engine blocks house pistons and cylinders, cylinder heads contain spark plugs, camshafts, and valves.
Cushioned between them, a head gasket acts as a seal resisting leakage of engine fuel and pressure losses. Placed on the cylinder head, it creates a barrier between the oil and the coolant.
Head gaskets perform certain functions that directly sync in improving the service life of an automobile engine. Here is a detailed overview:
This is the principal task of a gasket. It confines the combustion chamber allowing your vehicle to produce sufficient compression. The ideal pressure accelerates the engine’s power.
Since a combustion chamber holds the fuel, it overheats while driving. A head gasket secures the cooling channels between the engine block and the cylinder head to maintain an optimal temperature.
A gasket performs the crucial task of segregating the oil and coolant passages to prevent any mix-up. Not only does it resist any leakage, but it also repels the risk of detonation.
Being made after extensive research and using premium quality materials, a gasket is rigid and comes with an enduring operational life. However, certain conditions can trigger premature failure of a gasket.
Let's understand the reasons behind the breakdown first before moving to the consequences:
This is the most accepted cause of gasket failure. When an engine gets too hot to handle, it damages the gasket. The excessive heat can also deform the chamber head or block, making it unable for a gasket to seal.
Pre-ignition is a condition when the fuel and compressed air or refrigerant accidentally mix up, resulting in a spark. Inarguably, this is another reason behind an untimely blown gasket. It creates acute emphasis on the gasket leading to its premature failure.
Since a head gasket has thermal properties, it expands and collapses as per the engine temperature. Activating an engine and immediately ceasing it results in sudden temperature changes that pessimistically affect the lifespan of a gasket.
Similar to other existing components, ageing is another reason behind a blown gasket. After covering a significant mileage, it is recommended to replace the gasket. If unchanged, then it may lead to serious damage as the sealing power of a gasket wears out with time.
Last but not least, if a gasket has not been installed correctly, then it will not be able to last for a long time. Imprecise installation attracts premature failure. Moreover, incorrectly equipped gaskets are unable to seal the cylinder head properly, increasing the risk of detonation.
As per the condition's gravity, motorists can encounter several symptoms. Some of them are as follows:
Leakage of oil and coolant is the most noticeable sign when it comes to blown head gaskets. When a gasket fails to seal properly, fuel and refrigerant ooze from the engine block.
A faulty gasket can no longer keep the coolant and oil separated. Thus, the refrigerant leaks into the cylinder and disbalances the oil and air ratio resulting in a misfire.
As a sequel to the previous symptom, when the coolant burns in the cylinder, it turns into a composition of white smoke and water vapour and releases through the vehicle's exhaust. Hence, the egression of white vapour from your car's tailpipe is another sign of head gasket failure.
If you have experienced any of the enlisted symptoms, then look at the dipstick. If the oil has transformed into a whitish/milky shade, then the coolant has already blended with the oil. It also leaves residue on the oil filler cap.
The cost of a gasket depends on several factors. The manufacturer, applicable vehicle, and materials used play a crucial role in the price determination of a gasket. In India, the average cost of a head gasket ranges from ₹500 to ₹12000. Though the prices may seem a bit expensive, fixing a blown gasket is worthwhile as it secures the engine from further damage.
Hopefully, this piece has mended all your queries about a head gasket. This small yet significant element of a car’s engine keeps the coolant and oil separated and unmixed. Overheating of an engine or incorrect installation can decrease a gasket’s lifespan. Thus, proper maintenance of the engine will secure an extensive operational period for the gasket.
The service life of a gasket can vary depending on its material type, age, maintenance frequency, and engine condition. However, generally, it should run for approximately 100,000 miles.
The service life of a gasket can vary depending on its material type, age, maintenance frequency, and engine condition. However, generally, it should run for approximately 100,000 miles.
Replacement of a gasket requires the utmost knowledge and years of expertise. An average person may find it extremely difficult and time-consuming. Unless you are an ex-technician and have all prerequisite tools within reach, it is best to fix blown head gaskets at service centres.
Replacement of a gasket requires the utmost knowledge and years of expertise. An average person may find it extremely difficult and time-consuming. Unless you are an ex-technician and have all prerequisite tools within reach, it is best to fix blown head gaskets at service centres.
The ideal way to resist the premature failure of a head gasket is by keeping the engine coolant at the recommended level. In case you find coolant residue on the garage floor or ground, it is best to take your car for a check-up.
The ideal way to resist the premature failure of a head gasket is by keeping the engine coolant at the recommended level. In case you find coolant residue on the garage floor or ground, it is best to take your car for a check-up.
Please try one more time!
Other Important Articles About Different Car Parts
Other Important Articles about Car Insurance
Have queries related to Digit motor insurance policy? You can refer to our Policy Wordings for detailed information or reach out to our support team via WhatsApp self-support, email or phone using the information below:
Connect with our self-serve chat bot support - 7026061234
Write to us at hello@godigit.com
Contact
Call us on 1800-258-5956
Other Motor Insurance Plans and Guides
Currently there are no news to show.
Read More
Renew & Download Policy Document, Check Challan, Credit Score, PUC & more
Anytime, Anywhere. Only on Digit App!

4.7
Rated App56K+ Reviews
4.7
Rated App
56K+ Reviews
4.3
Rated App11K+ Reviews
4.3
Rated App
11K+ Reviews
Scan to Download


Author: Team Digit
Last updated: 07-04-2025
CIN: L66010PN2016PLC167410, IRDAI Reg. No. 158.
Go Digit General Insurance Limited | Corporate Office Address: Atlantis, 95, 4th B Cross Road, Koramangala Industrial Layout, 5th Block, Bengaluru 560095 | Registered Office Address: 1 to 6 floors, Ananta One (AR One), Pride Hotel Lane, Narveer Tanaji Wadi, Shivaji Nagar, Pune-411005, Maharashtra | Trade logo of Go Digit General Insurance Ltd. displayed above belongs to Go Digit lnfoworks Services Private Limited and is provided and used by Go Digit General Insurance Ltd. under license.
Explore exclusive features, file claims & access policy on Digit App!
You can also scan this QR code to download the App.