10 Diseases Caused by Drinking Less Water

Mica Sood, Pediatric NP at Tangipahoa Community Health Center in Hammond, LA, says that drinking adequate amounts of water is essential for maintaining hydration as it helps to improve the function of your brain, heart and muscles.
The top five benefits of drinking water include –
- Drinking water relieves fatigue and increases energy
- It promotes weight loss
- Water flushes out the waste and toxins from the body
- It improves the complexion of the skin
- Water helps in the digestion of foods and prevents constipation
Drinking water helps in the overall functioning of the human body. Therefore, every individual needs to drink an adequate amount of water daily to avoid the diseases caused by drinking less water.

Table of Contents

What is Dehydration?
Dehydration occurs when the body loses more fluids than it has taken in, thereby leading to insufficient water for normal functioning. In addition, it can result from drinking less water than your body needs, mostly in hot weather or during some physical activity.
Early signs are thirst, dry mouth, and dark urine. If uncorrected, dehydration can cause dizziness, tiredness and confusion. Drinking enough water daily to maintain overall health and stay hydrated is important.
What are the Causes of Dehydration?
Dehydration occurs primarily when the body loses more water than it takes in. The major cause of this is failure to drink enough water, which can occur due to several reasons:
- Insufficient Water Intake: Failing to drink an adequate quantity of water all day long, especially in hot weather or during exercise, may result in dehydration.
- Increased Fluid Loss: Exercising, sweating and spending time in a hot environment cause fluid loss. This is because lost fluids must be restored.
- Infection: Diseases such as fever, vomiting, diarrhoea and extensive urination might make a person lose more water than usual during these periods.
- Dietary Factors: Drinking too much alcohol or caffeine can also dehydrate you by acting as diuretics that promote excessive fluid loss from the body system.
- Age: Aging often leads to less drinking as not feeling thirsty anymore with age reduces intake of liquids among old people.
When someone drinks below his/her hydration needs, an imbalance of fluid results, leading to dehydration with its potential consequences.
10 Diseases Caused by Drinking Less Water in Humans
Drinking insufficient water can lead to several serious health conditions. Proper hydration is essential for maintaining bodily functions and preventing diseases that arise from dehydration. The diseases caused by drinking less water and their symptoms are:
1. Eczema
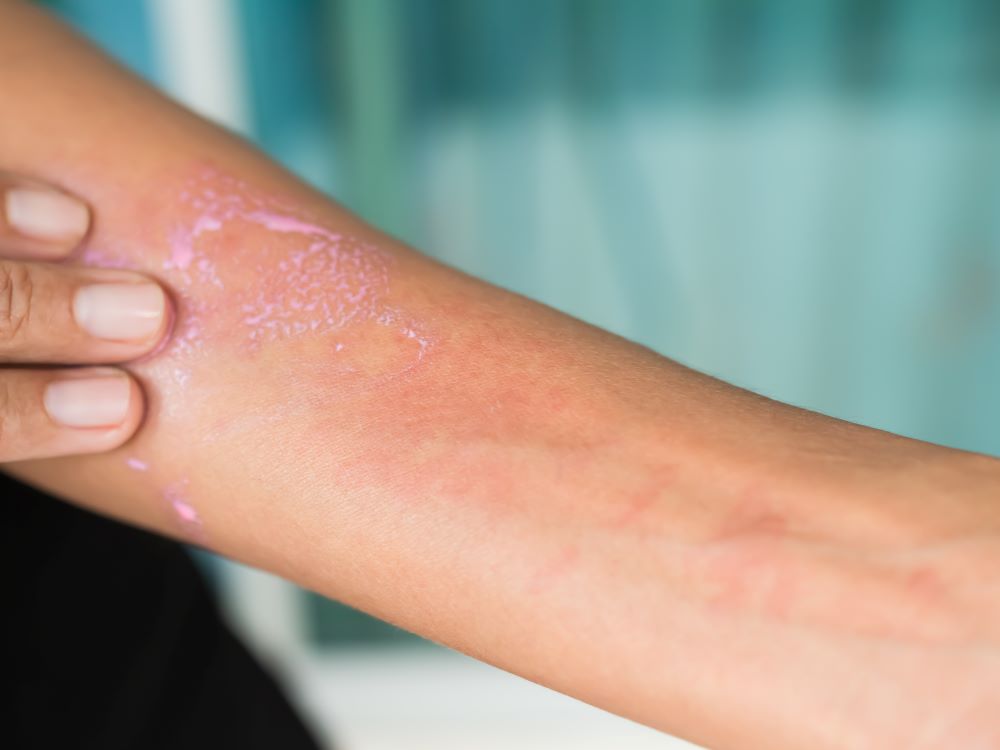
A human body requires an adequate amount of water for sweating out 500-700 ml of water. The sweat secreted by the sweat glands, carry out the toxins and waste from our body. If you do not drink enough water, these waste products do not come out of the body and cause skin irritation such as eczema.
Symptoms – Dry and itchy skin, bumps on the skin, red rashes, scaly and leathery patches of skin, crusting skin and swelling.
2. Fluctuation in Blood Pressure
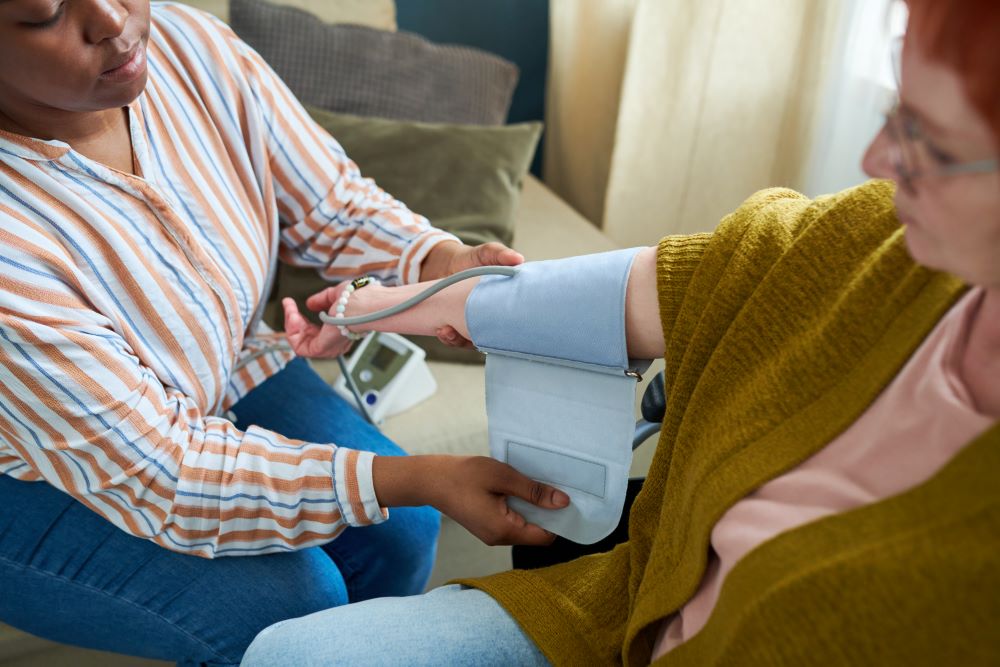

needs an adequate amount of water for overall functioning. Blood pressure fluctuations can result from stress, lifestyle changes, or underlying health conditions. These fluctuations can increase the risk of cardiovascular issues and require careful monitoring
.Symptoms – Severe headaches, nosebleeds, fatigue, chest pain, vision problems, irregular heartbeat, blood in urine, and difficulty breathing.
3. Urine Infection
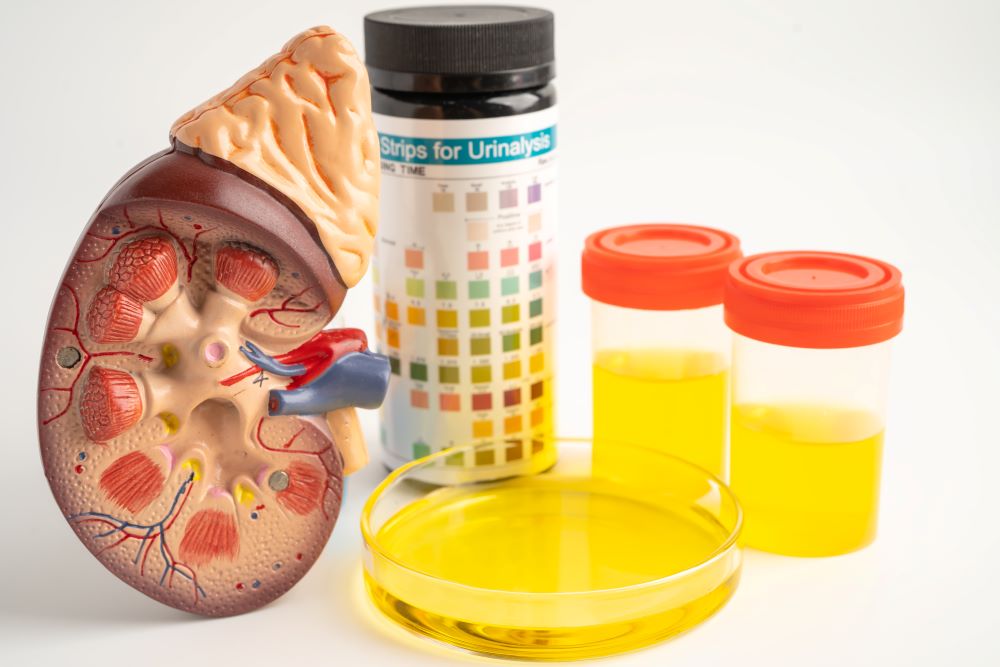
One of the significant side effects of drinking less water is urine infection. UTIs can affect any part of the urinary system, including the urethra, bladder, ureters, and kidneys. A urine infection occurs when bacteria enter the urinary tract, causing pain, frequent urination, and discomfort. If left untreated, it can lead to more severe complications, such as kidney infections.
Symptoms – Burning sensation during urination, dark and smelly urine, strong urge to urinate and urine appears cloudy.
4. Gastritis and Ulcers
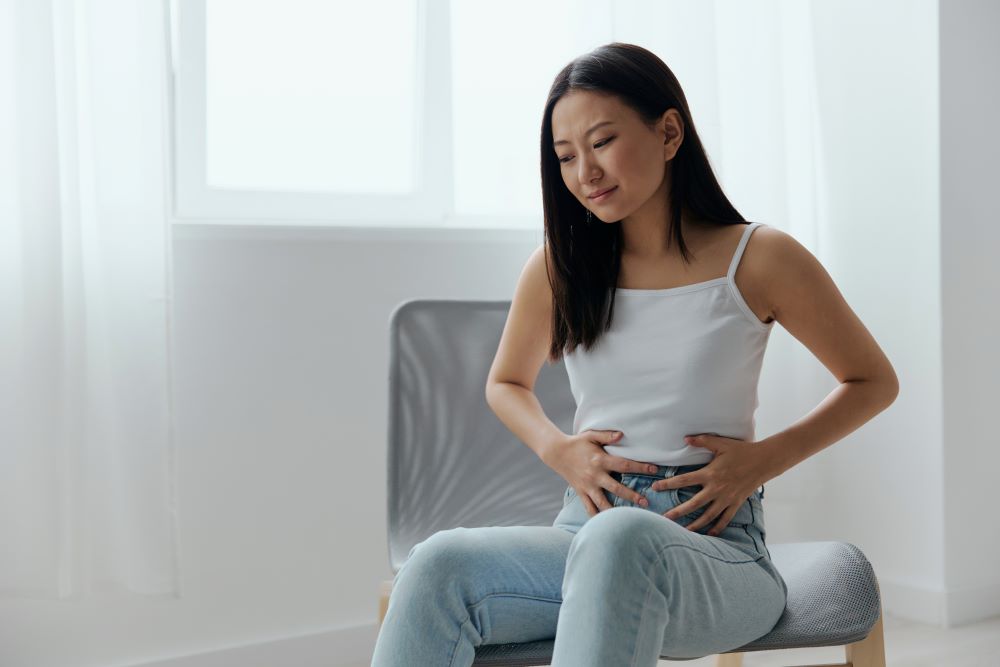

When the body is dehydrated, the production of digestive juices is lower. This results in diseases like gastritis and ulcers. Gastritis involves inflammation of the stomach lining, often leading to discomfort and indigestion. Ulcers are open sores that develop in the stomach or intestines, often due to excessive acid production.
Symptoms – Nausea, abdominal bloating, abdominal pain, vomiting, indigestion, burning feeling in the stomach, hiccups and loss of appetite.
5. Obesity
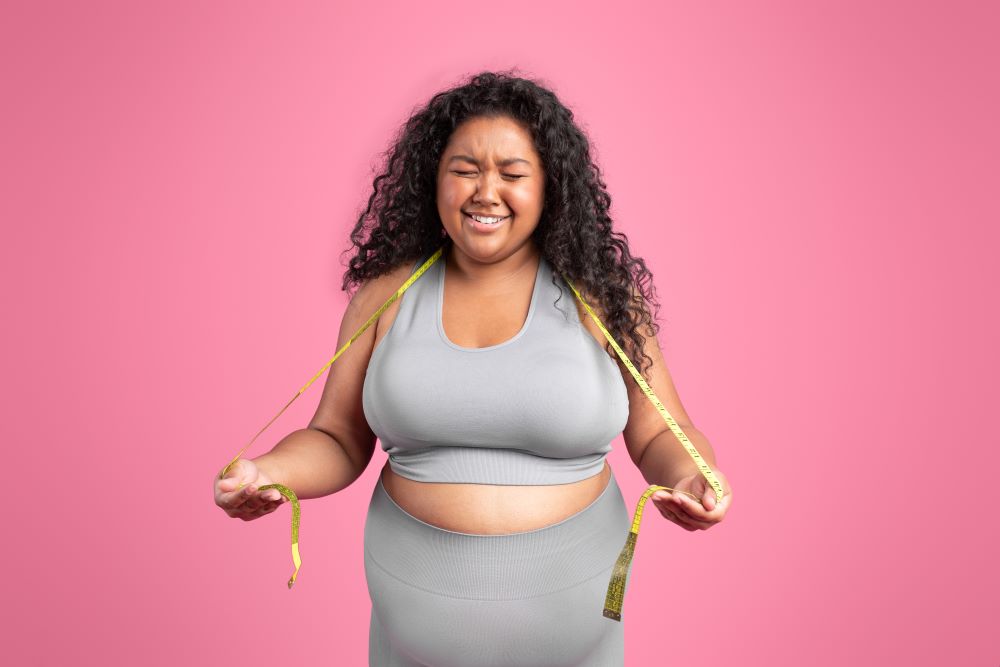

Due to the lack of water, there is a loss of energy, and the body feels tired. To cater to this feeling, we tend to eat more, leading to weight gain, leading to increased risk of chronic diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancers. It is often linked to lifestyle factors and requires comprehensive management.
Symptoms – Excess body fat, shortness of breath, snoring, trouble sleeping and not being able to perform simple physical tasks.
6. Kidney Stones
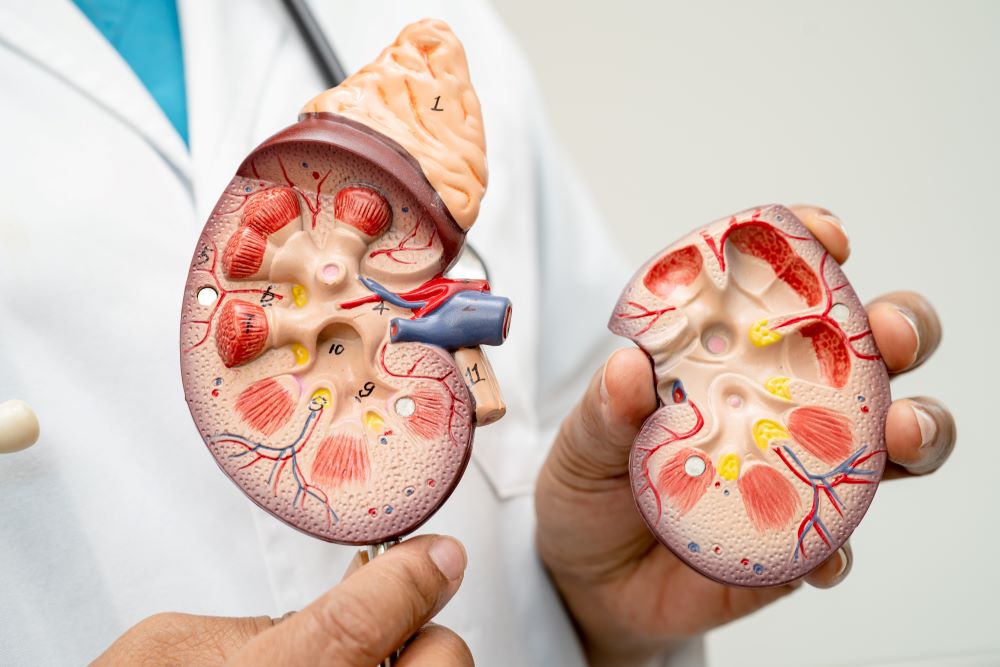
Kidney stones are hard mineral and salt deposits that form inside the kidneys. They develop when urine becomes concentrated, allowing minerals like calcium and oxalate to stick together, causing severe pain and discomfort when they pass through the urinary tract. They can be influenced by diet, dehydration, and certain medical conditions.
Symptoms: Severe pain in the lower back or side, blood in the urine, nausea, and frequent urination.
7. Chronic Constipation
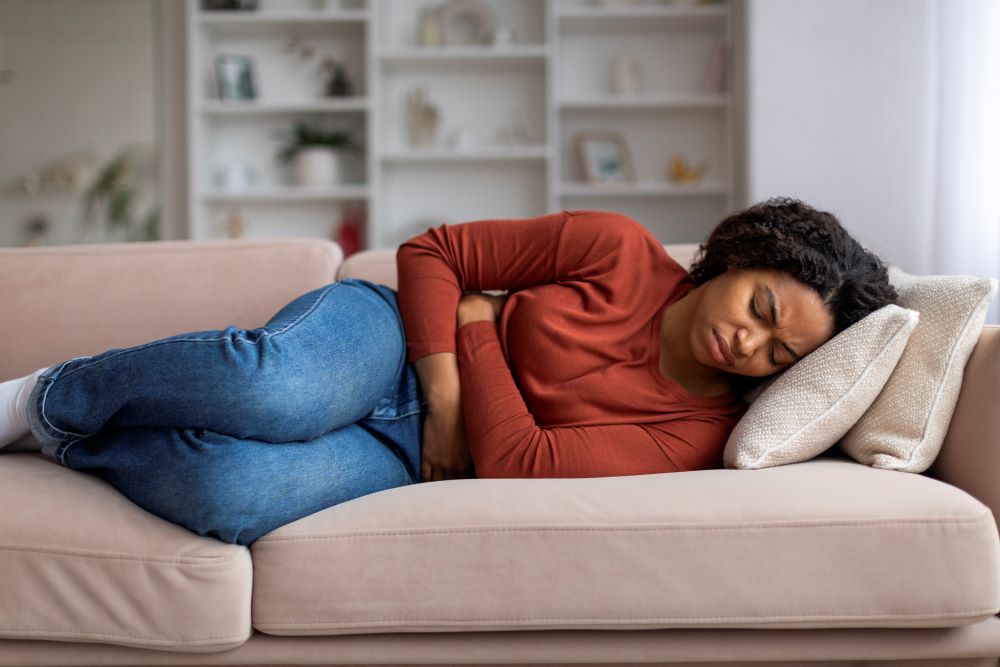

Water is essential for smooth bowel movements. When the body is dehydrated, the colon absorbs more water from waste, leading to hard and dry stools. This can cause chronic constipation, making bowel movements infrequent and difficult.
Symptoms: Persistent fatigue and swelling in the feet and ankles. Nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, and changes in urination patterns.
8. Skin Disorders
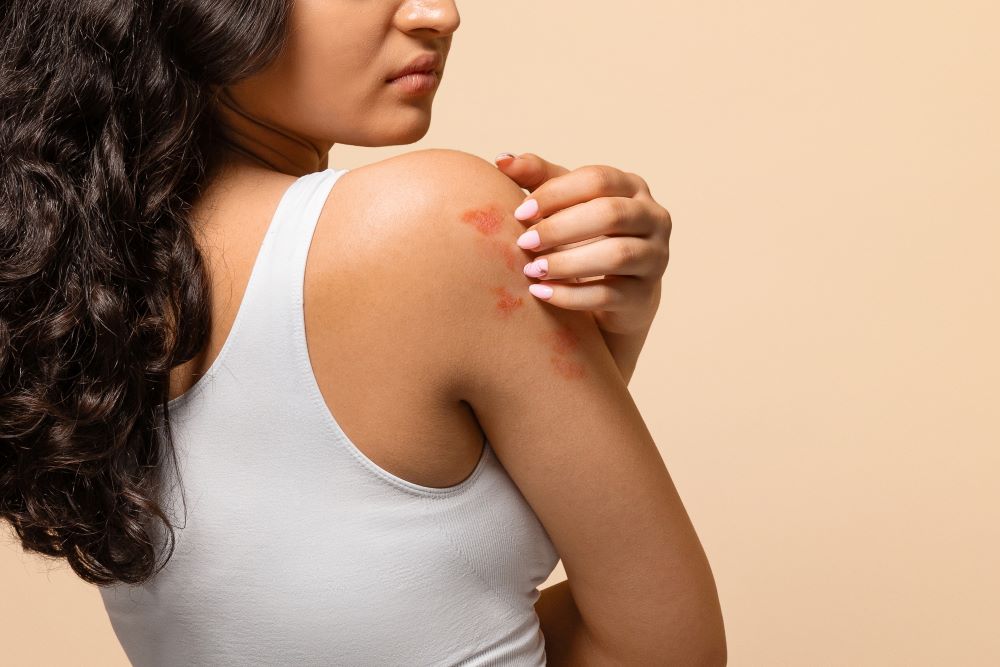
Dehydration reduces skin elasticity and moisture, leading to dry, flaky, and irritated skin. Chronic dehydration can exacerbate skin conditions such as eczema and psoriasis. Proper hydration keeps the skin healthy and resilient against environmental stressors.
Symptoms: Dry, flaky, or itchy skin, often accompanied by redness. Cracked, rough patches and increased sensitivity to environmental factors.
9. Headaches
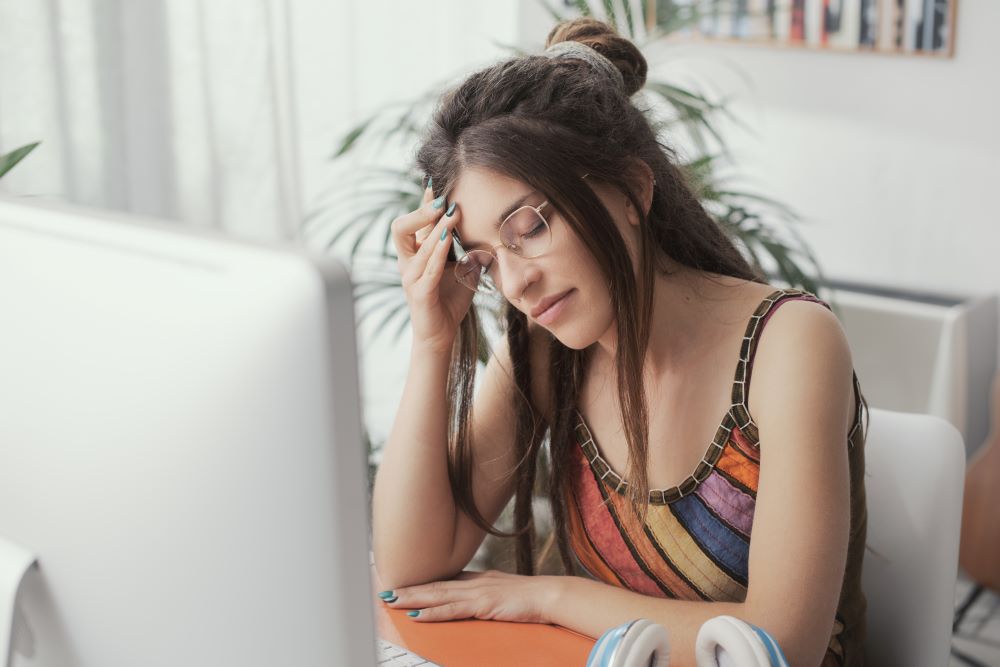

Dehydration can cause headaches due to reduced blood flow and oxygen to the brain. It can also lead to the narrowing of blood vessels in the brain, triggering a headache. Staying hydrated can prevent these headaches from occurring.
Symptoms: Throbbing or pressure-like pain, often around the forehead, temples, or back of the head. It may be accompanied by dizziness or sensitivity to light and sound.
What Are the Harmful Effects of Diseases Caused by Drinking Less Water?
In this section, we are going to throw some light on the harmful effects diseases caused due to drinking less water -
- Eczema – Higher odds of skin and other infections, depression, anxiety, sepsis and infection in the cornea of the eye may lead to blindness.
- Fluctuating blood pressure – Atherosclerosis, heart attacks, stroke, and significant changes in blood pressure can affect blood vessels in the brain.
- Urine Infection – Recurrent infections, kidney damages, kidney scars and hypertension.
- Gastritis and Ulcers – Stomach ulcer, stomach bleeding, stomach cancer anaemia, MALT lymphoma, stricture, renal problems, bowel obstruction and gastric cancer.
- Obesity – Type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, stroke, sleep apnea, hypertension, liver and gallbladder diseases and certain cancers.
Risk Factors Associated With Diseases Caused by Drinking Less Water?
Inadequate water intake increases the risk of various health conditions. Understanding these risk factors helps in the prevention and management of dehydration-related diseases.
How to Diagnose Diseases Caused by Drinking Less Water?
Understanding the signs that you are not drinking enough water is the key to preventing the diseases caused by drinking less water.
Let us see how to diagnose the diseases arising due to drinking less water –
What Is the Treatment for Diseases Caused by Drinking Less Water?
Treatment for diseases caused by drinking less water focuses on restoring adequate hydration and addressing related health issues. The diseases caused by drinking less water can be treated in the following ways:
- Eczema: Moisturising the skin twice daily, applying anti-itching cream to the affected regions, avoiding scratching, taking warm baths and using mild soaps without perfumes or dyes.
- Fluctuating Blood Pressure: Losing weight, exercising daily, consuming less sodium, avoiding stress, reducing caffeine and alcohol intake and cutting down on tobacco. A proper alternative is consuming foods that are rich in these minerals or supplements.
- Urine Infection: Antibiotics and cranberry juice. Flushing out bacteria from the urinary tract and preventing another infection can be aided by taking enough water. One should aim to consume between 8-10 glasses of water daily.
- Gastritis and Ulcers: Taking antacids to reduce stomach pain, avoiding spicy and hot foods, vitamin B12 shots, proton pump inhibitors, triple therapy, bismuth and H2 blockers produces less mucus, which protects the stomach lining from acidic digestive juices.
- Obesity: Healthy and balanced diet, daily physical activity, weight-management programs, weight-loss medicines and bariatric surgery. One’s metabolism and appetite control could be affected, hence contributing to weight gain and obesity.
What Are the Preventive Measures to Control Diseases Caused by Drinking Less Water?
The side effects of drinking less water can be prevented by drinking adequate amounts of fluid every day. The U.S. National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine suggest that an adult male should drink 3.7 litres of water daily. In contrast, an adult woman should drink at least 2.7 litres of the same every day to avoid discrepancies due to lack of water consumption.
Bowel movement, precipitation, breathing and urination causes loss of water from the human body. Therefore, it is essential to replenish the loss of water by drinking an adequate amount of fluid every day. This helps in the smooth and proper functioning of all the body parts. Failing to abide by this can lead to the aforementioned diseases caused by drinking less water.
Does Health Insurance Cover Disease Caused by Drinking Less Water?
Coverage of health insurance for diseases resulting from reduced water consumption varies with the specific policy in question and the nature of the ailment. Most health insurance plans cover medical treatment for diseases that occur as a result of dehydration, such as renal stones, urinary tract infections and heat stroke, since these are considered to be severe medical emergencies or essential, contributing cases.
However, routine treatments or preventive care related to hydration might not be covered. Read through your policy details or consult an agent who will advise you on what is included.
Some policies may include nutritionist consultations or preventive health services if they are medically necessary.
Drinking less water can result in dehydration, kidney stones, urinary tract infections, and electrolyte disorders. Early identification of symptoms is vital for good health. Diseases can be avoided by lifestyle changes such as drinking more water and helping one’s body perform its crucial functions. Periodic testing and knowledge about how much you need to drink are the key to preventing the consequences of insufficient hydration over a long period.














