Diseases Caused by Cockroaches, their Symptoms & Treatment

Not all diseases come from genetic history; some are rooted in the kitchen, pantry and are caused by cockroaches. Cockroach-borne diseases do not come to mind as easily as rodent-borne diseases, but cockroaches are a health hazard in the home environment. These insects are considered as allergen sources that trigger asthma and have the capability to carry disease-causing germs. The following sections cover every important detail about diseases caused by cockroaches. Read along!
Causes of Diseases Caused By Cockroaches
The transmission of cockroach-borne diseases involves various factors, some of which are related to the existence and behaviours of these insects.
- Food and Surface Pollution: Cockroaches traverse dirty regions, carrying germs and other contaminants onto foodstuffs and surfaces. This, in turn, results in salmonellosis, E. coli infections, etc., due to the consumption of contaminated foods.
- Allergens: Parts of a roach's body, excrement, or even saliva contain bacteria that can activate allergies or asthma, especially among people with weaker immune systems. Thus, one must be thorough while cleaning one's surroundings.
- Physical Contact: Living near cockroach-infested areas can result in the transmission of severe diseases like dysentery, Leprosy, and gastroenteritis from one person to another. Sanitation and cleanliness are key to avoiding ailments.
14 Diseases Caused by Cockroaches in Humans
Cockroaches are responsible for spreading a wide range of diseases. Unlike mosquitos, the spreading methods are not direct; thus, transmission can occur indirectly through consumption or contact with items with cockroaches that are contaminated with bacteria.
Following is a list of diseases caused by cockroaches,
1. Campylobacteriosis
Campylobacteriosis is caused by bacteria known as Campylobacter jejuni. This pathogen can be spread by cockroaches that pass away some human food and other things. Symptoms include diarrhoea, compounded by abdominal pain, high temperature, and vomiting. The disease usually resolves within a week of occurrence, but in serious cases, complications can arise.
2. Cholera
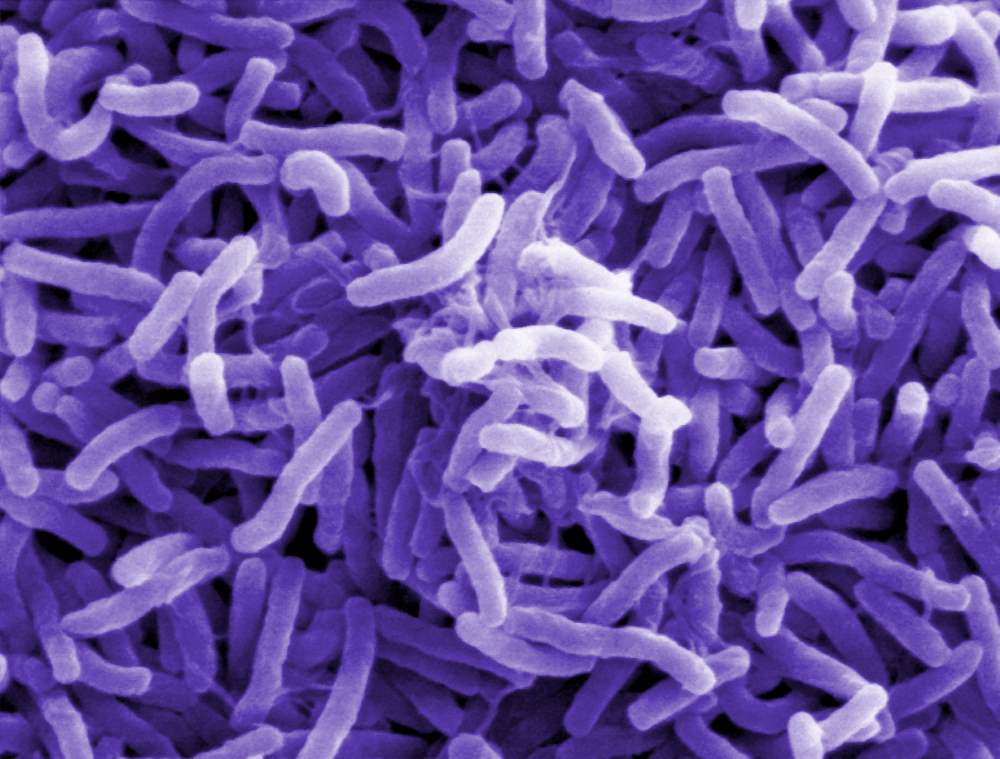
Cholera is an infectious disease resulting from the bacterium Vibrio cholerae, which is mainly transmitted through contaminated waterways. Nevertheless, roaches are also implicated in contaminating water or food supplies, hence their distribution. It mostly causes heavy watery diarrhoea, which leads to dehydration in victims.
3. Leprosy
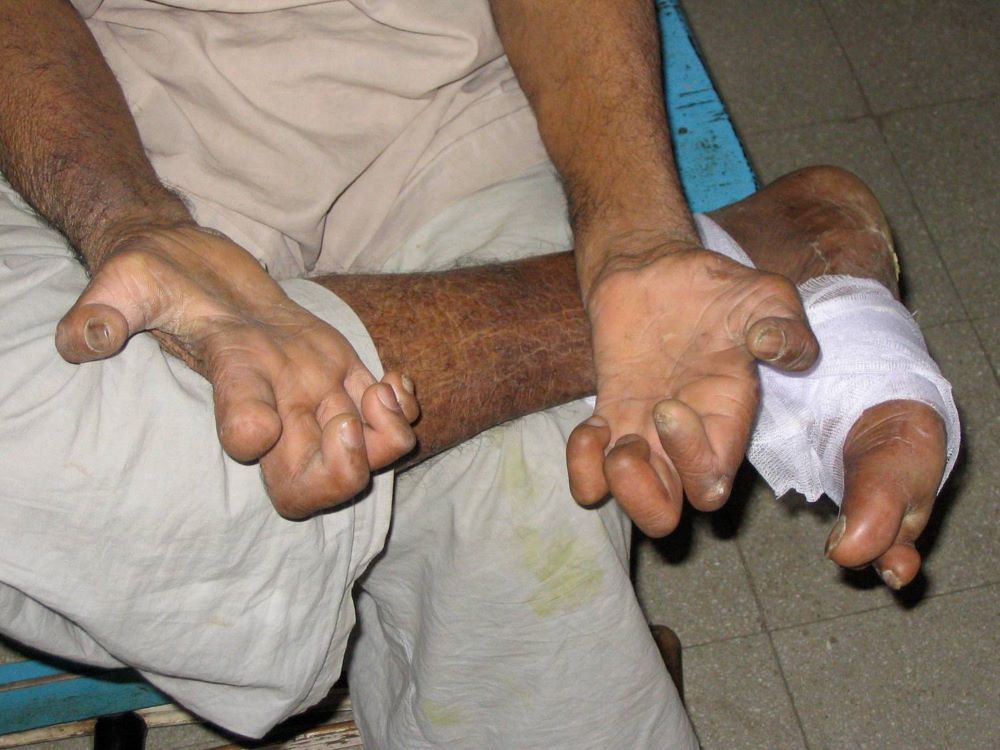
Mycobacterium leprae is responsible for Leprosy, also known as Hansen's Disease. In addition, filthy surroundings may provide a conducive environment for cockroaches, hence promoting Leprosy through poor hygienic practices. Leprosy includes skin lesions, nerve damage, and muscle weakness, among other things.
4. Dysentery

Among these pathogens are Shigella bacteria, like amoebas, such as Entamoeba histolytica, which cause dysentery. Cockroaches transmit such germs via infected foods or surfaces. Severe diarrhoea with blood in stool, abdominal pains, and fever characterise the infection. Effective treatment takes course for over 90% of those affected, and most recover fully.
5. Listeriosis

Listeriosis results from infection by a bacterium, Listeria monocytogenes. The ailment normally ranges from mild flu-like symptoms to severe occurrences such as meningitis or sepsis, particularly in pregnant women, the elderly, infants, and persons with weak immune systems. For severe cases of this condition, antibiotics are required.
6. Salmonellosis
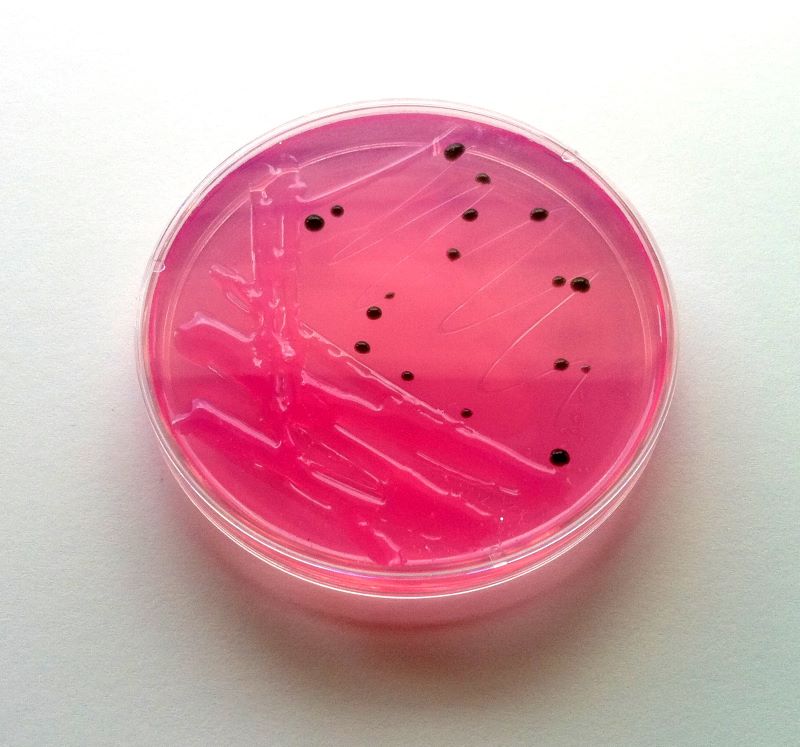
Salmonellosis is caused by a bacteria called salmonella. Roaches can spread this bacterium through their faeces or when they contaminate food. Symptoms include diarrhoea, stomach pains, fevers, and nausea. While most instances will resolve themselves without any need for medical care, in other cases, however, antibiotic treatment may be necessary.
7. Gastroenteritis
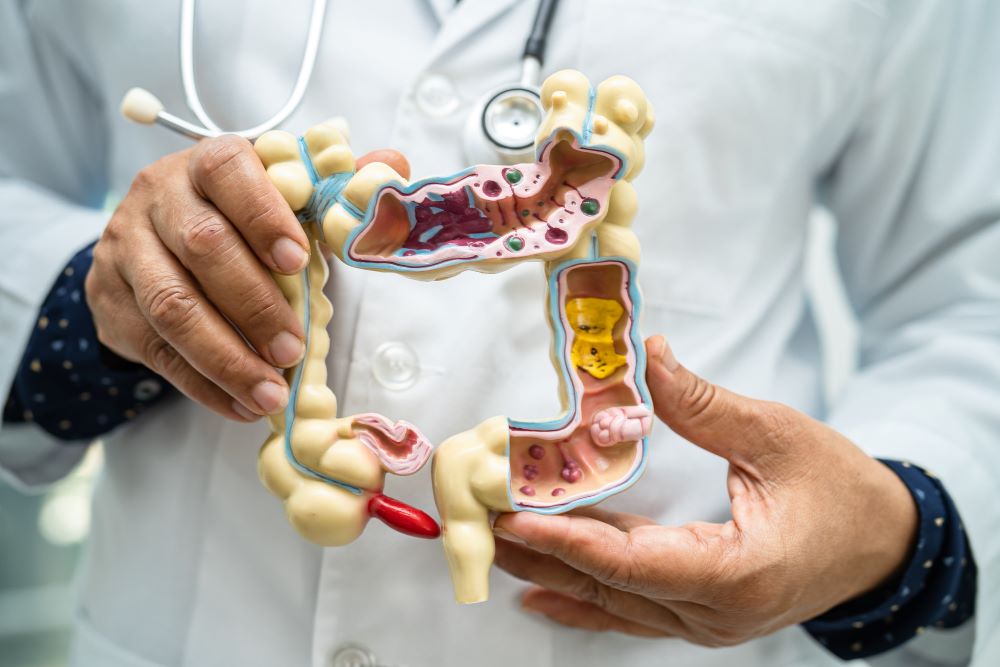
This is an infection that causes inflammation of the intestines and stomach due to various pathogens, including viruses, bacteria, and parasites. In addition, roaches transmit these organisms pathogenetically, which leads to signs like vomiting, diarrhoea, bellyache, and feverishness.
8. Giardia

Giardiasis is caused by a parasite known as Giardia lamblia. Furthermore, roaches become carriers of giardiasis, thus facilitating its transmission through water and food contamination. Commonly reported symptoms consist of diarrhoea, abdominal pain, tummy problems, and loss of weight. Antiparasitic drugs (e.g., metronidazole or tinidazole) are prescribed for treatment.
9. Typhoid Fever
Typhoid fever is caused by a bacterium known as Salmonella Typhi. Cockroaches can disseminate this pathogen indirectly through food or water contamination, especially in unhygienic conditions. The indications of the disease are a lasting high temperature, general debility, pain in the bowels, and rashes in the skin.
Apart from these, cockroaches can cause other health issues such as:
10. Asthma

Asthma attacks can be initiated by cockroach allergens found in their faeces, saliva, or body parts. This is mostly seen among children and those with existing respiratory conditions. These allergens cause inflammation and blockage of airways, leading to wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath.
11. E. coli Infection
When spread by cockroaches, this bacterium can contaminate food and surfaces. Diarrhoea (sometimes bloody), abdominal cramps, nausea, and vomiting are signs of E. coli infections that can develop after consuming contaminated food or drink. Severe cases can lead to kidney failure or hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS).
12. Staphylococcus Aureus
Staphylococcus aureus bacteria on cockroaches could trigger an infection in people, leading to boils or abscesses in the skin. Once these infections become severe, they spread throughout the body, resulting in sepsis. Redness, swelling, and pain would be typical symptoms, while systemic infection might present with fever, chills, and overall malaise.
13. Allergies

The faeces, saliva, and body parts of cockroaches contain allergens that can trigger allergic reactions and even asthma. For example, this can lead to rhinitis (sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes) or dermatitis (skin rash and itching). Cockroach-susceptible individuals may experience deterioration in symptoms as the level of exposure rises.
14. Streptococcus
Cockroaches can harbour streptococcus bacteria, leading to infections such as strep throat or skin conditions like impetigo. Symptoms of strep throat include a severe sore throat, fever, and swollen lymph nodes, while skin infections cause redness, swelling, and pain. Prompt treatment with antibiotics is necessary to prevent complications.
Now, let’s move on to learn about symptoms, harmful effects, prevention methods, and many more.
What Are Common Bacteria Borne By Cockroaches?
Cockroaches are known carriers of various harmful bacteria. Understanding the specific bacteria they can harbour helps address potential health risks associated with infestations.
What Are the Harmful Effects of Diseases Caused by Cockroaches?
The diseases caused by cockroaches have specific harmful effects, such as bubonic plague that caused 584 reported deaths between 2010-2015 as per data published by WHO. The link between plague and cockroaches might surprise some individuals since rodents usually carry this disease. However, cockroaches can be responsible for spreading the Yersinia pestis bacterium that can cause bubonic plague.
Diseases like Streptococcus can result in mild throat infection, or in worst cases, it can lead to severe infection of blood and organs.
On the other hand, if pregnant women get affected by the disease of Listeriosis, it can sometimes result in miscarriage, premature delivery or, in worst cases, stillbirth.
Asthma can have a severe impact on certain individuals. Cockroaches carry protein in their body which can trigger allergic reactions and asthma. Asthma can severely impact the airways of the lungs and can affect both children and adults.
What Are the Symptoms of Diseases Caused by Cockroaches?
Depending on the disease, symptoms of cockroach-borne diseases can also vary. However, some generic signs and symptoms include,
- Fever: A familiar response to infection, fever indicates the body’s attempt to fight off disease-causing organisms that enter through cockroaches. It usually occurs together with other signs, such as chills and sweat.
- Muscle and Joint Pain: These pains may arise from inflammations of infections caused by bacteria transmitted by cockroaches. They can be experienced as pain or stiffness, especially in more severe cases.
- Diarrhoea: Foodstuffs and surfaces contaminated by cockroaches may cause intestinal diseases, such as diarrhoea, marked by frequent and watery stools accompanied by dehydration and debility.
- Nausea or Vomiting: Stomach inflammations resulting from irritants in cockroaches can make a person puke because of gastric irritation. This is often accompanied by a lack of appetite and an upset stomach.
- Chesty Cough: Inhaling allergens or pathogens found on cockroach droppings or body parts can severely inflame the passage, leading to chronic coughing that produces mucus.
- Shortness of Breath: Respiratory problems may result from allergies or infections originating from cockroaches, leading to a feeling of being unable to breathe correctly, particularly among individuals with underlying diseases like asthma.
- Wheezing: This sound, which resembles a pitched whistle during breathing, is most frequently a result of inflammation in the airways due to allergies or infections brought about by roach contact.
What Are the Risk Factors for Diseases Spread by Cockroaches?
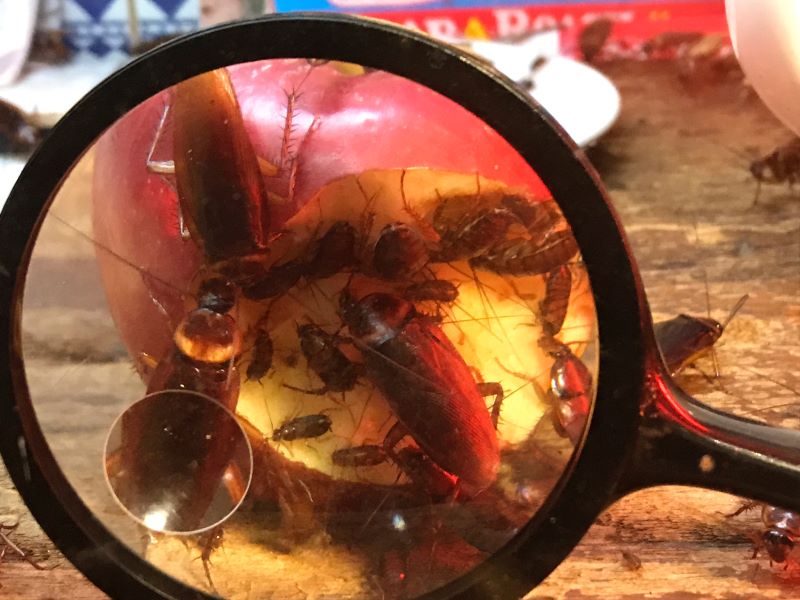

Cockroaches are a sign of poor hygiene. Hence, if individuals, especially pregnant women, live in an unhealthy home environment, it will increase the chance of developing cockroach borne diseases such as Listeriosis or Asthma and other gastronomical diseases.
How to Diagnose Diseases Caused by Cockroaches?
To diagnose diseases caused by cockroaches, doctors can follow the methods discussed below:
What Are the Treatments for Diseases Caused by Cockroaches?
Treatment of cockroach caused diseases may vary depending on the type of disease. However, doctors can prescribe
1. Antibiotics
Doctors prescribe antibiotics to kill bacteria or inhibit their growth in bacterial infections like campylobacteriosis, leprosy, or salmonellosis. These medications are necessary to halt the spread of infection and reduce its severity.
2. Intravenous or Oral Hydration
For illnesses such as cholera and dysentery that may lead to dehydration, intravenous fluids or oral rehydration solutions may replace lost fluids and electrolytes. This crucial treatment modality ensures that normal fluid homeostasis is maintained.
3. Prescription Medications for Allergies
- Cromolyn Sodium: This drug makes mast cells stable, so they cannot release histamine and other chemicals, which cause allergic reactions.
- Desensitisation Treatments: Allergy shots or sublingual tablets are administered progressively to reduce allergic responses with time.
- Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists: These drugs prevent leukotrienes, substances that cause inflammation and allergy symptoms in asthmatics.
4. Over-the-Counter Medications
- Decongestants: These reduce nasal congestion by narrowing blood vessels in the nasal passages, helping to ease breathing.
- Antihistamines: They block the effects of histamine, a substance in the body that causes allergic symptoms like itching, swelling, and runny nose.
- Nasal Corticosteroid Sprays: These anti-inflammatory sprays reduce swelling and mucus production in the nasal passages.
What Are the Preventive Measures to Control Diseases Caused by Cockroaches?
To prevent diseases that spread due to cockroaches, individuals have to follow the tips mentioned below,
- Clean work and cooking surface on a regular basis
- Wash dishes, utensils immediately after using
- Clean food remnants after eating
- Maintain hygiene and wash hands frequently
- Seal cracks and crevices in kitchen, windows, bathrooms and other cockroach entry points
- Store food in an airtight container
The above-mentioned piece provides a complete guide on diseases caused by cockroaches. Individuals must read these details carefully, clean the kitchen and work surface properly and control cockroaches to prevent diseases spread by these insects.
Does Health Insurance Cover Disease Caused by Cockroaches?
Depending on the terms of the health insurance policy, cockroach-borne diseases are usually included. Normally, such coverage provides for doctor visits, lab tests, and drugs like antibiotics for infections or allergy medications following exposure to roaches.
Nonetheless, the coverage level will depend on your policy's provisions, and some plans may require the fulfillment of certain conditions or exclude particular treatments. Therefore, it is important to carefully review your health care policy to know what is covered regarding disease from contact with cockroaches.
Proper knowledge of the diseases and health risks associated with cockroach infestations is crucial for effective prevention and control. The above-mentioned piece provides a complete guide on diseases caused by cockroaches. Individuals must read these details carefully, clean the kitchen and work surfaces properly, and control cockroaches to prevent diseases spread by these insects.
















