8 Diseases Caused by Obesity & How to Prevent Them

Obesity is a health condition that happens due to the accumulation of excess body fats in a certain part of the body. This condition may lead to several other diseases.
It is a major risk factor for numerous health issues, affecting millions worldwide. Understanding these diseases and how to prevent them is crucial for maintaining overall health. Continue reading to know what diseases are caused by obesity.

Table of Contents

What are Obesity Diseases?
Overweight-related conditions are health issues that emanate from having too much body fat. They include heart disease, type 2 diabetes, some kinds of cancer, and sleep apnea. Obesity puts more pressure on the systems and organs within the body, leading to long-term illnesses.
This is often associated with lifestyle aspects such as poor nutrition, sedentary behaviors, and genetic inheritance. Maintaining a healthy weight by living right is crucial in eliminating these diseases. For example, someone can be obese if he/she is overweight because of his/her genetics, lack of physical activity, or unhealthy diet.
What are the Causes of Obesity Diseases?
Obesity is mysterious and has numerous causes. It’s essentially an imbalance between calorie intake and energy expenditure that leads to excess fat storage. Significant contributors include poor nutritional practices such as high-calorie, low-nutrient eating habits and lack of physical activity.
Genetics, hormonal imbalances, and other medical conditions are among the causes of obesity. Additionally, psychological factors such as stress and emotional eating tend to make it worse. Understanding these causes becomes crucial in preventing obesity-related diseases.
What Are the Diseases Caused by Obesity?
Individuals suffering from obesity have several conditions. Some of the diseases caused by obesity are
Stroke and Heart Diseases

People who are overweight or obese are prone to high cholesterol and high blood pressure. These conditions make an individual more susceptible to heart disease and stroke. Over time, the cartilage breaks down, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
The accumulation of fat around the heart contributes to these risks. Managing weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help reduce these risks.
Type 2 Diabetes
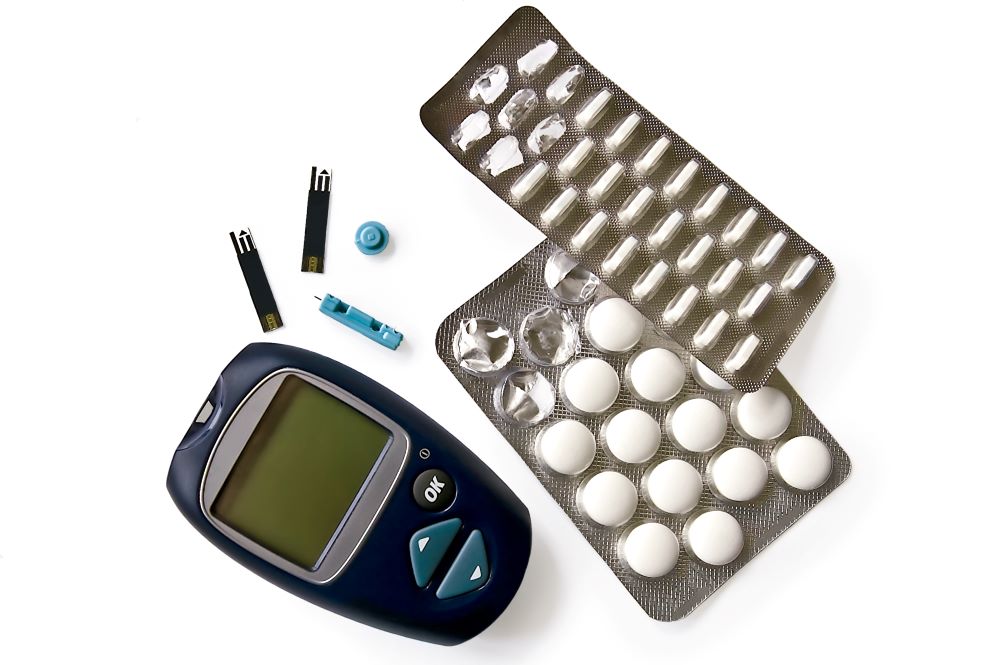
It is one of the most common diseases associated with obesity. This happens because of inflammation and an increase in the level of fatty acids. Obesity is closely linked to gout because excess body weight can lead to higher uric acid levels, where the body’s cells do not respond properly to insulin. This results in higher blood sugar levels
Weight loss, improved diet, and regular physical activity are essential for preventing and managing type 2 diabetes.
Certain Types of Cancer

Obesity causes cancer such as the breast (after menopause), colon, kidney, endometrium, and oesophagus. The relationship between obesity and cancer is complex. The relationship between obesity and cancer involves factors like increased inflammation, hormone levels, and insulin resistance.
Maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, and staying active can help lower the risk of these cancers.
Gallstones and Gallbladder Diseases
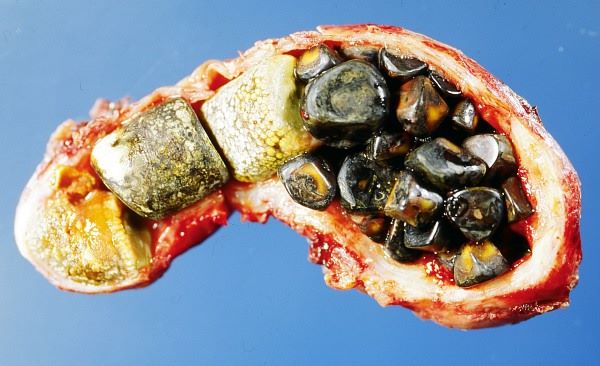
These are very common if you have obesity. Ironically, rapid weight loss itself can cause the formation of gallstones. Therefore, consider losing weight at a rate of about one pound per week to avoid gallstones, which are solid particles that form in the gallbladder. Rapid weight loss can also lead to gallstone formation.
To minimise risk, aim for gradual weight loss of about one pound per week and maintain a balanced diet rich in fibre and low in unhealthy fats.
Osteoarthritis

The extra weight puts additional pressure on the knee joints of individuals and damages the cartilage that protects them. These anomalies gradually cause osteoarthritis, a common, degenerative joint disease that occurs when the cartilage is cushioning.
Weight management is crucial for slowing the progression of osteoarthritis and alleviating symptoms.
Gout

It is a condition that affects the joints. Gout happens when the uric acid levels in the blood increase, and this disease is common among people with obesity. When uric acid accumulates, it forms sharp, needle-like crystals in the joints, causing intense pain and inflammation.
Managing weight, staying hydrated, and avoiding foods high in purines (like red meat and alcohol) can help control and prevent gout.
Sleep Apnea
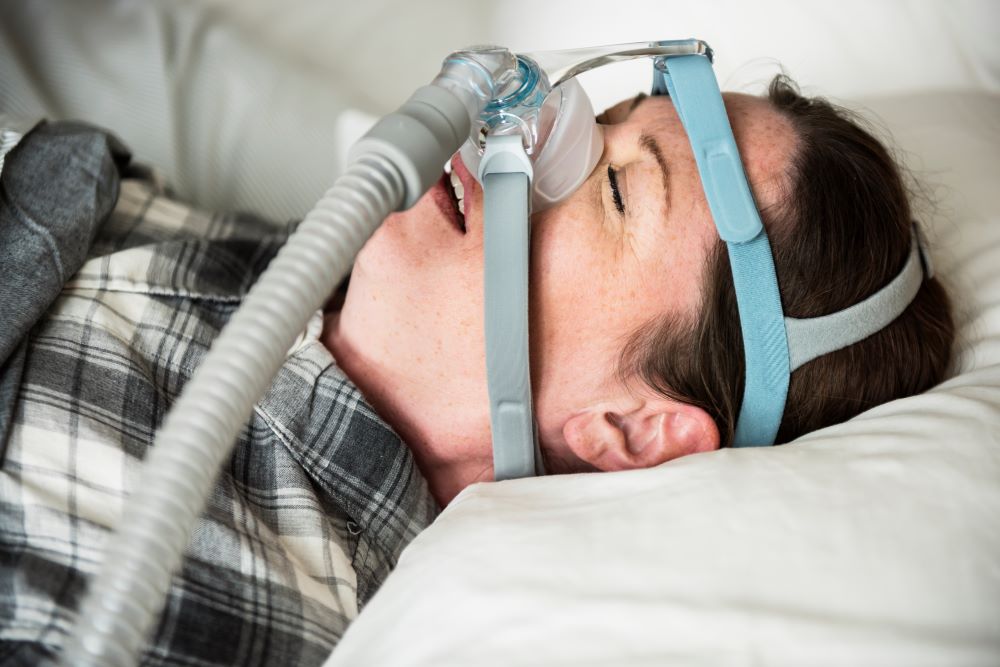
Due to the fat deposit, the upper tract of the respiratory system narrows significantly. Thus, the muscle activities in this region decrease, resulting in sleep apnea. Sleep apnea can result in poor sleep quality and increased risks of heart disease, hypertension, and stroke.
Weight loss, lifestyle changes, and using a CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure) machine can help manage sleep apnea.
Asthma

According to the American Lung Association, excess accumulation of weight around the abdomen and chest constricts the lungs and makes it difficult to breathe. Therefore, asthma is one of the many diseases due to obesity. Excess weight can also exacerbate symptoms and reduce the effectiveness of asthma medications.
Maintaining a healthy weight and managing asthma through medication and lifestyle adjustments can improve symptoms and overall respiratory health.
Now that you know about the diseases caused by obesity, let’s move on to the risk factors.
Signs and Symptoms of Diseases Caused by Obesity
Frequent signs and symptoms usually accompany diseases caused by being overweight, which can affect different body parts. Identifying these early is important so they can be well managed and complications prevented.
- Joint Ache and Rigidity: Obesity causes joint pain, among other things, due to increased pressure on weight-bearing joints such as those found in the knees and hips. The result is chronic pains, stiffness, and limited mobility.
- Altered Breathing Patterns: In this case, excess fat, particularly around the neck area, narrows the breathing passage, leading to obstructive sleep apnea. This sleeping disorder causes pauses in breathing during slumber, which can lead to snoring and tiredness.
- Heightened Blood Pressure: Obesity commonly leads to high blood pressure (hypertension) because it increases a person’s heart workload. Continuously high blood pressure is a critical risk factor for heart attacks and strokes.
- Raised Sugar Levels in the Bloodstream: Insulin resistance often links obesity with type 2 diabetes, causing abnormally increased blood sugar levels. This results in various symptoms like constant exhaustion, excessive thirst, or urination patterns.
- Chronic Fatigue: Obesity-related conditions, such as diabetes mellitus and sleep apnea, may lead to unrelenting fatigue. Such consistent fatigue affects everyday activities and the general quality of life.
Damages Caused by Obesity in Humans

Obesity is known to have far-reaching consequences for human health, leading to different kinds of physical and metabolic harm. Recognising these effects is central to addressing the risks that are associated with being overweight.
- Cardiac Damage: Obesity heightens the danger of heart disease through increasing blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, and plaque build-up within arteries. This adds strain to the heart’s structures, making it vulnerable to heart attacks and heart failure.
- Respiratory Problems: Extra fat, especially around the abdomen and neck, may impede airways and reduce lung function. Moreover, it results in complications such as obstructive sleep apnea, whereby individuals stop breathing momentarily while asleep.
- Musculoskeletal & Joint Issues: The burden posed by extra kilos affects joints, most especially knees, hips, and lower backs; this quickens cartilage wear away, resulting in osteoarthritis accompanied by long-term pain.
- Metabolic Disorders: Obesity is a major contributor to metabolic syndrome. Elevated levels of fatty acids and inflammation from excess weight disrupt the body's ability to regulate blood sugar, leading to an increased risk of diabetes and related complications.
- Increased Cancer Risk: Obesity is associated with a higher risk of several cancers, including breast, colon, and endometrial cancers. Excess body fat can lead to hormonal imbalances and chronic inflammation, both of which contribute to cancer development.
Risk Factors Associated With Diseases Caused by Obesity
Obesity significantly increases the risk of developing various diseases through several interconnected factors. Understanding these risk factors is crucial for preventing and managing obesity-related conditions effectively.
How is Obesity Disease Diagnosed?

Diagnosing obesity involves a range of assessments to evaluate body weight, composition, and related health conditions. Accurate diagnosis helps in understanding the extent of obesity and planning appropriate treatment strategies.
Treatment Methods for Obesity Diseases
The prevention and management of these diseases often require effective treatment methods, such as:
- Lifestyle Modifications: Lifestyle modifications are foundational in treating obesity-related diseases. These include adopting a balanced diet rich in nutrients, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress.
- Pharmacological Treatments: Pharmacological treatments may be prescribed to assist with weight loss and manage obesity-related conditions. Medications such as appetite suppressants or metabolic enhancers can be added to changes in one’s way of life.
- Surgical Interventions: Several surgical interventions, such as bariatric surgery, may benefit individuals who are extremely obese or have not had much success with other approaches.
- Integrated Care Approaches: Integrated care approaches entail a multidisciplinary team approach to tackling obesity and its related diseases. This team includes professionals such as nutritionists and exercise physiologists.
What Are the Preventive Measures to Control Diseases Caused by Obesity?
The diseases caused by obesity can be avoided by following the preventive measures for obesity. Let us take a look at how to prevent obesity for kids and adults.
Preventing Obesity for Kids
Following practices can prevent obesity in kids -
- A study conducted by WHO showed that breastfeeding can lower the chances of obesity in a child by up to 25%.
- Following a healthy diet regularly.
- Eating slowly and only when you are hungry.
- Remove unhealthy foods from the house.
- Encourage exciting and fun physical activities.
- Ensure that your kid is getting enough sleep.
Preventing Obesity for Adults
Adults can prevent obesity in the following ways –
- Limit the consumption of bad fats such as saturated and trans fats
- Eat less processed and sugary foods.
- Incorporate adequate amounts of vegetables and fruits into your diet.
- Eat low glycemic index foods.
- Engage yourself in daily aerobic activities.
- Do not take stress unnecessarily.
People who have psychological conditions like depression, anger, etc., are more likely to get obese or overweight. Therefore, individuals suffering from such issues must exercise, do yoga, or go out for a bicycle ride to keep their minds stress-free. Preventing obesity is the key to avoiding the diseases caused by obesity.
Does Health Insurance Cover Obesity Diseases?
Health insurance coverage for obesity-related diseases varies by policy and location. Most plans cover illnesses like type 2 diabetes, heart disease, or high blood pressure, which are usually associated with being overweight. However, some medical covers do not cover weight loss interventions or medication designed solely to manage obesity.
To know the content, one needs to review what is outlined in his/her policy. One should carefully peruse their specific terms before conferring with their insurer.
The significant health impact of obesity on the human body results in various serious diseases. To avoid these illnesses, obesity must be addressed by changing the way people live their lives, for instance, following a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight. One should always consider one's weight for long-term well-being and health while focusing on overall wellness.














