Road Tax in Tamil Nadu & Vehicle RTO Charges in 2025

The magnificent state of Tamil Nadu is home to many attractions, like the ancient temple town of Madurai, the breezy and serene coastline of Mahabalipuram, and the mist-covered hill village of Kodaikanal.
If you own and use a car in the state, you must pay the statutory road tax charged by the Central Motor Vehicles Act of 1988.
Continue reading to know more about road tax in Tamil Nadu and vehicle RTO charges.

Table of Contents

What is Road Tax?
Road tax is a mandatory fee imposed by governments on vehicles that use public roads to fund the maintenance and development of road infrastructure. It is typically paid annually or semi-annually, and the amount varies based on factors such as the type of vehicle, its engine size, and its age.
Vehicles with larger engines or higher emissions often face higher taxes, while older vehicles might be taxed differently from newer ones. Road tax is required to ensure that vehicles are legally allowed to operate on public roads.
How is Road Tax Calculated?
Tamil Nadu vehicle tax is calculated on the various make, models and purpose of use of the vehicles, engine capacity, registered seating capacity of the vehicle and more. The law that governs it is the Tamil Nadu Motor Vehicle Taxation Act of 1974. Citizens also need to service a Green Tax applicable in the state.
Road Tax for Two Wheelers in Tamil Nadu
The tax rate for two-wheelers is determined by the vehicle's price or weight when purchased new and its worth when transferred from another state.
The following table displays the road tax in Tamil Nadu for two-wheelers:
| Type of Two-wheeler | Annual Road Tax |
| Moped with unladen weight below 90.72 kg | ₹500 |
| Price of two-wheeler up to ₹0.20 lakh | 5% of the two-wheeler’s price |
| Price of two-wheeler over ₹0.20 lakh and below ₹0.60 lakh | 7% of the two-wheeler’s price |
| Price of two-wheeler over ₹0.60 lakh and up to ₹2.00 lakh | 10% of the two-wheeler’s price |
| Price of two-wheeler exceeding ₹2.00 lakh | 12% of the two-wheeler’s price |
Road Tax for Four Wheelers in Tamil Nadu
Four-wheeler vehicles in Tamil Nadu are taxed based on their price, much as two-wheelers. Tamil Nadu's road tax for automobiles and other four-wheelers is as follows:
| Type of Four-wheeler | Annual Road Tax |
| Cars priced up to ₹6.00 lakh | 9% of the car’s value |
| Cars priced between ₹6.00 lakh and 10.00 lakh | 12% of the car’s value |
| Cars priced between ₹10.00 lakh and 20.00 lakh | 18% of the car’s value |
| Cars priced above ₹20.00 lakh | 20% of the car’s value |
Road Tax for Commercial Vehicles in Tamil Nadu
Commercial vehicles in Tamil Nadu are subject to different road tax levies than private or government vehicles. These tax rates are also calculated based on engine size, such as ton.
The table below shows the payload capacity of commercial vehicles and their tax:
| Loading capacity of commercial vehicle | Annual Road Tax |
| Not more than 1 ton | ₹600 |
| Above 1 ton and below 2 ton | ₹950 |
| Above 2 ton and below 4 ton | ₹1,500 |
| Above 4 ton and below 6 ton | ₹1,900 |
| Above 6 ton and below 8 ton | ₹2,100 |
| Above 8 ton and below 9 ton | ₹2,300 |
| Above 9 ton and below 10 ton | ₹2,500 |
| Above 10 ton | ₹3,000 |
Road Tax for Three Wheelers in Tamil Nadu
The purpose of the vehicle affects the three-wheeler road tax in Tamil Nadu. Check out the chart below for additional information:
| Type of Three-wheeler | Annual Road Tax |
| Passenger Vehicle (seating capacity below 12 | ₹600 per seat |
| Good Vehicles | ₹1,000 per Tonne or part thereof or ₹5,600 per Tonne or part thereof |
Road Tax for Other State Vehicle in Tamil Nadu
In Tamil Nadu, vehicles registered in other states are subject to road tax, depending on their type and the duration of their stay in the state. The Tamil Nadu government has also introduced an online system through the Parivahan portal to streamline vehicle tax payments from other states.
Here are some typical road tax rates for different types of vehicles:
| Type of Vehicle | Frequency of Tax Payment | Tax Rate |
| Light Goods Vehicles | Daily | ₹60 per day |
| Medium Goods Vehicles | Daily | ₹90 per day |
| Heavy Goods Vehicles | (minimum 12 days) | ₹120 per day |
| Non-AC Public Service Vehicles | Monthly (minimum 12 days) | ₹25 per day |
| AC Public Service Vehicles | Quarterly (minimum 30 days) | ₹35 per day |
How is the Road Tax in Tamil Nadu Calculated?
The Tamil Nadu Road tax depends on the following factors:
1. Type of Your Vehicle
The kind of vehicle is one of the most critical factors impacting the road tax. The road tax varies substantially depending on whether you own a two-wheeler, a four-wheeler, a three-wheeler, or a vehicle registered in another state.
Two-wheelers pay less road tax than larger cars.
Four-wheelers, such as vehicles and SUVs, pay greater taxes based on weight and engine capacity.
Tax rates for three-wheelers and automobiles registered in various states varied.
2. Purpose of Usage: Personal or Commercial
The amount of road tax owed depends on whether the vehicle is utilised for personal or business reasons.
Personal vehicles like family cars and motorbikes have lower tax rates.
Commercial vehicles, such as trucks, buses, and taxis, face higher road charges due to greater road wear and tear.
3. Engine Capacity
Another significant factor is engine capacity, measured in cubic centimetres (cc). Vehicles with bigger engine capacities are normally charged more.
Two-wheelers under 125 cc have lower taxes.
Larger engine vehicles like SUVs and luxury automobiles pay higher road taxes. This is because cars with larger engines are thought to contribute more to road traffic and environmental impact.
4. Type of the Model of Your Vehicle
The model type (regular, luxury, or sports) significantly impacts the tax rate. Luxury and high-end vehicles are taxed more heavily than basic models, reflecting their higher market value and additional maintenance costs to public infrastructure.
5. Fuel Type
The kind of gasoline used in your car also determines the tax amount. Vehicles with diesel, petrol, electrical or hybrid engines are taxed differently:
Diesel automobiles are often subject to higher levies owing to environmental concerns.
Governments may provide tax breaks or reductions for electric vehicles (EVs) as an incentive to promote environmentally friendly transportation.
6. Ex-Showroom Price of Your Vehicle
The ex-showroom price, or the car's price before taxes and insurance, is vital in determining road tax. Higher-priced vehicles incur higher road tax charges. As a result, luxury autos and premium two-wheelers pay more in unpaid road tax than cheaper models.
7. Seating Capacity
The number of passengers a vehicle may carry also affects road tax calculation, especially for commercial vehicles. Higher seating capacity vehicles, such as buses or multi-passenger vans, incur a higher road tax since they cause more road wear and are primarily used for business purposes.
How to Pay Road Tax in Tamil Nadu Online?
Paying your road tax online is a great way to avoid lengthy, unpleasant lineups. To pay your road tax online in Tamil Nadu, just follow these steps:
Step 1: Go to the official e-Vahan website, Ministry of Road Transport and Highways, and select the tax payment option.

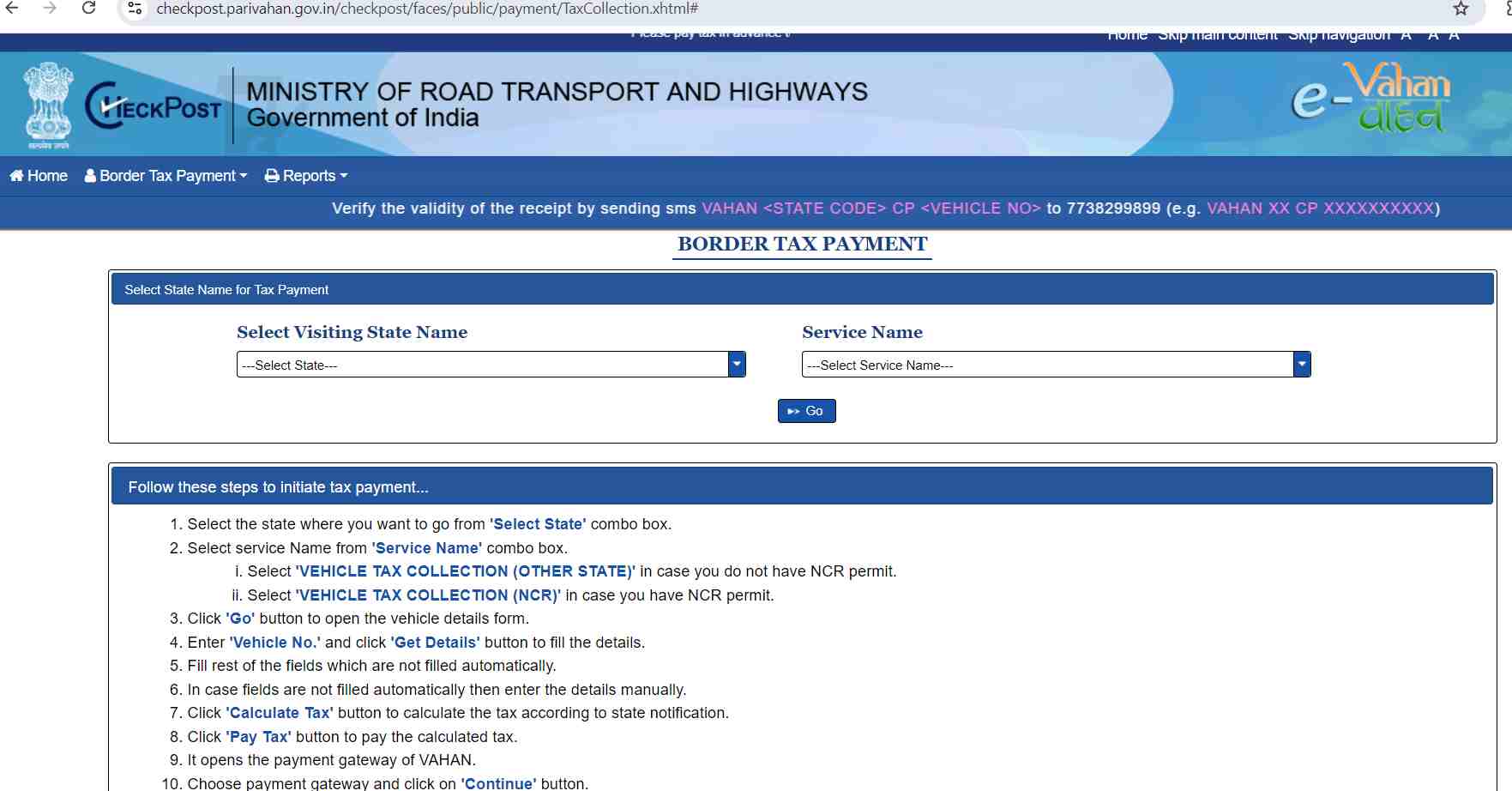
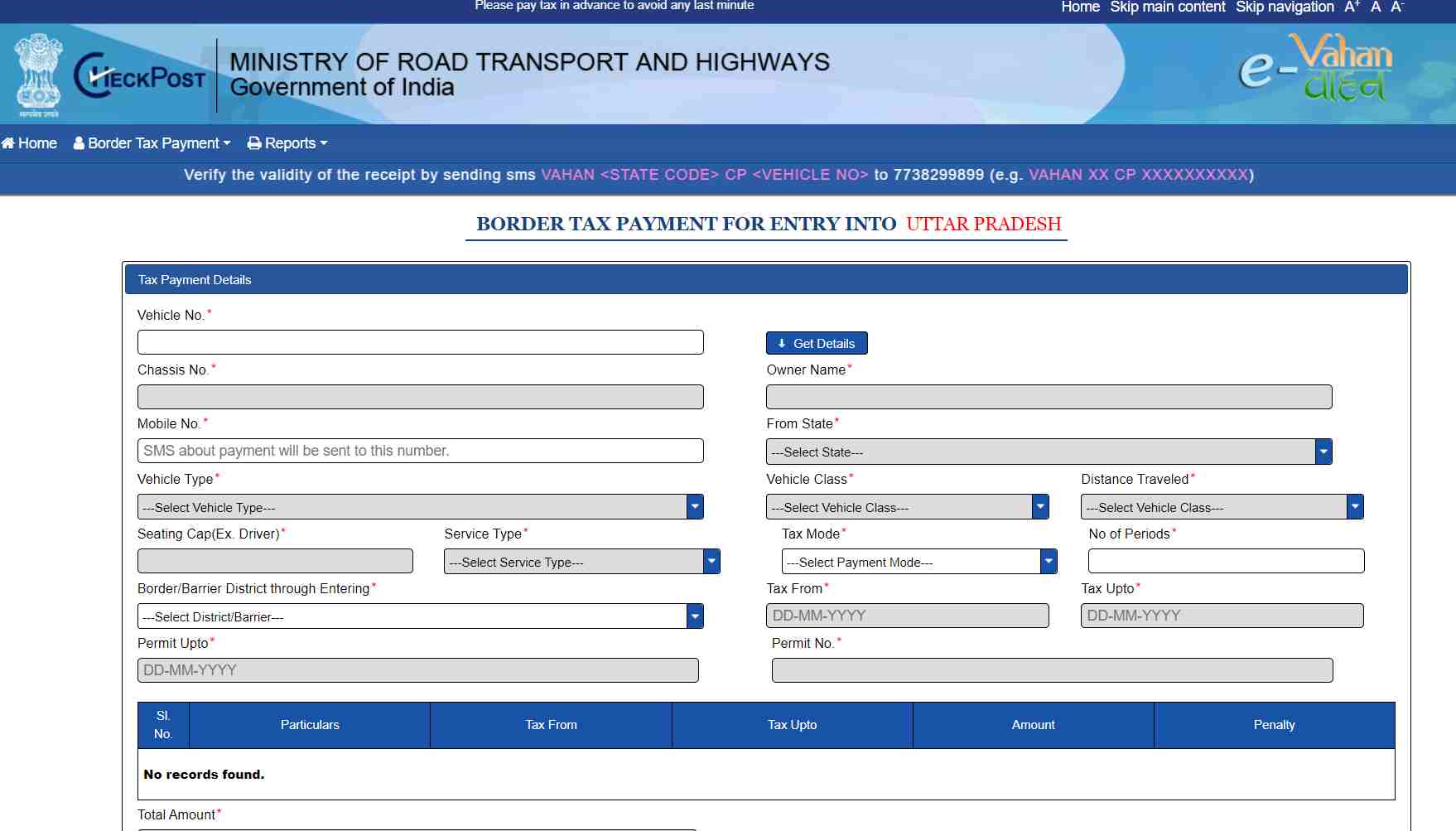
Step 3: You'll be sent to a new page. To complete the form, enter 'Vehicle No.' and click 'Get Details'.
Penalty for Not Paying Road Tax in Tamil Nadu
Vehicle owners in Tamil Nadu who do not pay road taxes face a fine equivalent to the unpaid road tax. Tamil Nadu may apply a 100% penalty in line with the legislation if taxes are paid for up to four weeks beyond the due date. If caught driving without paying the road tax, you risk having your automobile impounded for the offence.
List of RTOs in Tamil Nadu
The list has information on RTOs across the state to pay the Tamil Nadu Road tax:
| RTO Code | RTO Locations |
| TN-01 | Central |
| TN-02 | Anna Nagar |
| TN-03 | Tondiarpet |
| TN-04 | Pulianthoppu |
| TN-05 | Kolathur |
| TN-06 | Mandaveli |
| TN-07 | Thiruvanmiyur |
| TN-09 | KK Nagar |
| TN-10 | Virugambakkam |
| TN-11 | Tambaram |
| TN-12 | Paruthipattu |
| TN-13 | Ambattur |
| TN-14 | Sholinganallur |
| TN-15 | Ulundurpet |
| TN-15M | Kalakurichi |
| TN-16 | Tindivanam & Enforcement wing. |
| TN-18 | Redhills |
| TN-19 | Chenagalpattu |
| TN-20 | Thiruvallur |
| TN-21 | Kanchipuram |
| TN-22 | Meenambakkam |
| TN-23 | Vellore |
| TN-24 | Krishnagiri |
| TN-25 | Tiruvannamalai |
| TN-28 | Namakkal |
| TN-29 | Dharmapuri |
| TN-30 | Salem West |
| TN-31 | Cuddalore |
| TN-32 | Viluppuram |
| TN-33 | Erode |
| TN-34 | Tiruchengode |
| TN-36 | Gobi |
| TN-37 | Coimbatore South |
| TN-38 | Coimbatore North |
| TN-39 | Tirupur North |
| TN-40 | Mettupalayam |
| TN-41 | Pollachi |
| TN-42 | Tirupur South |
| TN-43 | Ooty |
| TN-45 | Trichy West |
| TN-46 | Perambalur |
| TN-47 | Karur |
| TN-48 | Srirangam |
| TN-49 | Thanjavur |
| TN-50 | Tiruvarur |
| TN-51 | Nagapattinam |
| TN-52 | Sangagiri |
| TN-54 | Salem East |
| TN-55 | Pudukkottai |
| TN-56 | Perundurai |
| TN-57 | Dindigul |
| TN-58 | Madurai South |
| TN-59 | Madurai North |
| TN-60 | Theni |
| TN-61 | Ariyalur |
| TN-63 | Sivagangai |
| TN-64 | Madurai Central |
| TN-65 | Ramanathapuram |
| TN-66 | Coimbatore Central |
| TN-67 | Virudhunagar |
| TN-68 | Kumbakonam |
| TN-69 | Tuticorin |
| TN-70 | Hosur |
| TN-72 | Tirunelveli |
| TN-73 | Ranipet |
| TN-74 | Nagercoil |
| TN-75 | Marthandam |
| TN-76 | Tenkasi |
| TN-77 | Attur |
| TN-78 | Dharapuram |
| TN-79 | Sankarankovil |
| TN-81 | Trichy East |
| TN-82 | Mayiladuthurai |
| TN-83 | Vaniyambadi |
| TN-83M | Tirupattur |
| TN-84 | Srivilliputtur |
| TN-85 | Kundrathur |
| TN-86 | Erode West |
| TN-87 | Sriperumbudur |
| TN-88 | Namakkal South |
| TN-90 | Salem |
| TN-91 | Chidambaram |
| TN-92 | Thiruchendur |
| TN-93 | Mettur |
| TN-94 | Palani |
| TN-95 | Sivakasi |
| TN-96 | Kovilpatti |
| TN-97 | Arani |
| TN-99 | Coimbatore West |













