Road Tax in Maharashtra & Vehicle RTO Charges in 2025

In Maharashtra, road tax is mandatory when registering a vehicle or applying for a renewal. The applicable fees are determined by the Regional Transport Office (RTO) and play a crucial role in developing and maintaining the state's road infrastructure.
In 2024, this state implemented an updated structure for road taxes and RTO charges to streamline the vehicle registration process and comply with national transportation norms.
Thus, if you are purchasing a new vehicle, renewing registration, or transferring ownership, having a clear idea of the applicable fees is a must to avoid penalties and legal complications.
Keep scrolling for a detailed insight on road tax in Maharashtra and the vehicle RTO charges.

Table of Contents

What is Road Tax?
Road tax is essentially a state-level tax on vehicle owners' use of public roads. It is payable during the vehicle registration process and can be a one-time or periodic payment.
The state uses these funds for the maintenance, improvement, and development of its roadways. The payable tax amount usually differs based on aspects like the vehicle’s engine capacity, type, weight, and other state-specific regulations.
Check out the tables below to get a comprehensive idea of the road tax rates in Maharashtra.
Road Tax for Two-Wheelers in Maharashtra
Road tax for two-wheelers in Maharashtra is calculated based on factors like the vehicle’s ex-showroom price. Also, the rates tend to differ based on whether you have a domestically manufactured two-wheeler or an imported one.
Get an overview of the vehicle tax on two-wheelers in Maharashtra in the table below:
Type of Two-Wheeler |
Annual Road Tax |
Motorcycles having engine capacity below 99 cc |
10% (minimum of ₹1,500) |
Motorcycles having engine capacity between 99 cc and 299 cc |
11% (minimum of ₹1,500) |
Motorcycles having engine capacity above 299 cc |
12% (minimum of ₹1,500) |
Imported motorcycles having engine capacity below 99 cc |
20% of the vehicle’s purchasing cost |
Imported motorcycles having engine capacity between 99 cc and 299 cc |
20% of the vehicle’s purchasing cost |
Imported motorcycles having engine capacity above 299 cc |
20% of the vehicle’s purchasing cost |
Road Tax for Four-Wheelers in Maharashtra
Road tax for four-wheelers in Maharashtra depends on the vehicle’s purchasing cost and fuel type. Find the applicable rates in the table below:
Type of Four-Wheeler |
Annual Road Tax |
Petrol Cars |
|
Vehicles with an ex-showroom price up to ₹10 Lakhs |
11% |
Vehicles with an ex-showroom price ranging between ₹10 Lakhs and ₹20 Lakhs |
12% |
Vehicles with an ex-showroom price above ₹20 Lakhs |
13% |
Diesel Cars |
|
Vehicles with an ex-showroom price up to ₹10 Lakhs |
13% |
Vehicles with an ex-showroom price ranging between ₹10 Lakhs and ₹20 Lakhs |
14% |
Vehicles with an ex-showroom price above ₹20 Lakhs |
15% |
LPG or CNG Vehicles |
|
Vehicles with an ex-showroom price up to ₹10 Lakhs |
7% |
Vehicles with an ex-showroom price ranging between ₹10 Lakhs and ₹20 Lakhs |
8% |
Vehicles with an ex-showroom price above ₹20 Lakhs |
9% |
Imported Cars |
|
Vehicles with an ex-showroom price up to ₹10 Lakhs |
20% |
Vehicles with an ex-showroom price ranging between ₹10 Lakhs and ₹20 Lakhs |
20% |
Vehicles with an ex-showroom price above ₹20 Lakhs |
20% |
Road Tax for Commercial Vehicles in Maharashtra
The road tax for commercial vehicles in Maharashtra is based on the vehicle type and ex-showroom price. As such automobiles are used commercially, they use more roads and thus have higher applicable rates compared to personal vehicles.
Listed below are the road tax charges in Maharashtra for commercial or transport vehicles:
| Vehicle Category | Road Tax Rates |
| Petrol Omni Buses | |
| Vehicles with ex-showroom price up to ₹10 Lakhs | 11% |
| Vehicles with ex-showroom price ranging between ₹10 Lakhs and ₹20 Lakhs | 12% |
| Vehicle with ex-showroom price above ₹20 Lakhs | 13% |
| Diesel Omni Buses | |
| Vehicles with ex-showroom price up to ₹10 Lakhs | 13% |
| Vehicles with ex-showroom price ranging between ₹10 Lakhs and ₹20 Lakhs | 14% |
| Vehicle with ex-showroom price above ₹20 Lakhs | 15% |
| Standees | ₹200 for every seat per year |
| Air-conditioned buses | ₹1,800 for every seat per year |
| Non-air-conditioned buses | ₹800 for every seat per year |
| LPG or CNG Vehicles | |
| Vehicles with ex-showroom price up to ₹10 Lakhs | 7% |
| Vehicles with ex-showroom price ranging between ₹10 Lakhs and ₹20 Lakhs | 8% |
| Vehicle with ex-showroom price above ₹20 Lakhs | 9% |
Road Tax for Three-Wheelers in Maharashtra
When it comes to three-wheelers, the road tax rate in Maharashtra depends upon the vehicle’s seating capacity. Moreover, the vehicle should be fitted with fare metres and used for carrying less than 6 passengers.
Find the applicable rates in the table below:
| Vehicle Category | Annual Road Tax |
| Vehicles with permission to carry up to 2 passengers | ₹11,000 |
| Vehicles with permission to carry up to 3 passengers | ₹13,200 |
| Vehicles with permission to carry up to 4 passengers | ₹17,600 |
| Vehicles with permission to carry up to 5 passengers | ₹22,000 |
| Vehicles with permission to carry up to 6 passengers | ₹26,400 |
How is the Road Tax in Maharashtra Calculated?
Road tax in Maharashtra is calculated based on the following parameters:
1. Vehicle Type
One of the primary factors that determine road tax calculation is the vehicle type. As a result, the amount of road tax you need to pay usually depends upon whether you have a two-wheeler, three-wheeler, car, or vehicles registered in other states:
Two-wheelers generally are taxed based on their engine capacity and their rates are generally lower than larger vehicles.
Four-wheelers (cars and SUVs) are taxed depending upon their fuel type and purchasing costs.
Three-wheelers are taxed based on their seating capacity.
Vehicles from other states are taxed based on their duration of stay in Maharashtra.
2. Engine Capacity
A vehicle’s engine capacity, measured in cubic centimetres (cc), is another essential factor when calculating road tax in Maharashtra. In this regard, vehicles with higher engine capacity generally attract higher taxes. Thus:
Two-wheelers having engine capacity below 125 cc usually have lower road tax.
Four-wheelers with larger engine capacities, like SUVs and luxury sedans, generally come with higher road tax.
3. Usage: Personal or Commercial
The amount of road tax payable also depends upon whether the vehicle is for personal or commercial usage:
Personal vehicles like, family cars, bikes, scooters, etc., have lower road tax rates and are payable on a one-time basis.
Commercial vehicles like buses, taxis and trucks have higher tax rates that are payable on an annual basis.
4. Fuel Type
The road tax rates also tend to differ based on the vehicle’s fuel type. Thus, depending upon whether your bike/car runs on petrol, diesel, CNG/LPG, or electricity, the tax rate will vary. In this regard:
Diesel-powered vehicles have higher road tax rates due to environmental concerns.
Electric vehicles (EVs) usually get road tax exemption at the time of registration due to the Government’s efforts to encourage eco-friendly transportation.
5. Type of Model
The model of your vehicle (standard, sports, or luxury) also tends to impact the road tax amount. Usually, luxury and high-end vehicle models attract higher taxes compared to the standard models due to their high market value.
6. Seating Capacity
In case of some commercial vehicles, the amount of payable road tax depends upon the passenger carrying capacity. Thus, automobiles with higher seating capacities, like buses and multi-passenger vans, generally have a higher road tax rate as they are primarily used for commercial use and cause higher wear and tear on public roads.
7. Ex-Showroom Price
Another crucial determinant of road tax is the vehicle’s ex-showroom price. As a result, higher-priced automobiles like high-end luxury cars and imported motorcycles come with higher road tax rates.
How to Pay Road Tax in Maharashtra Online?
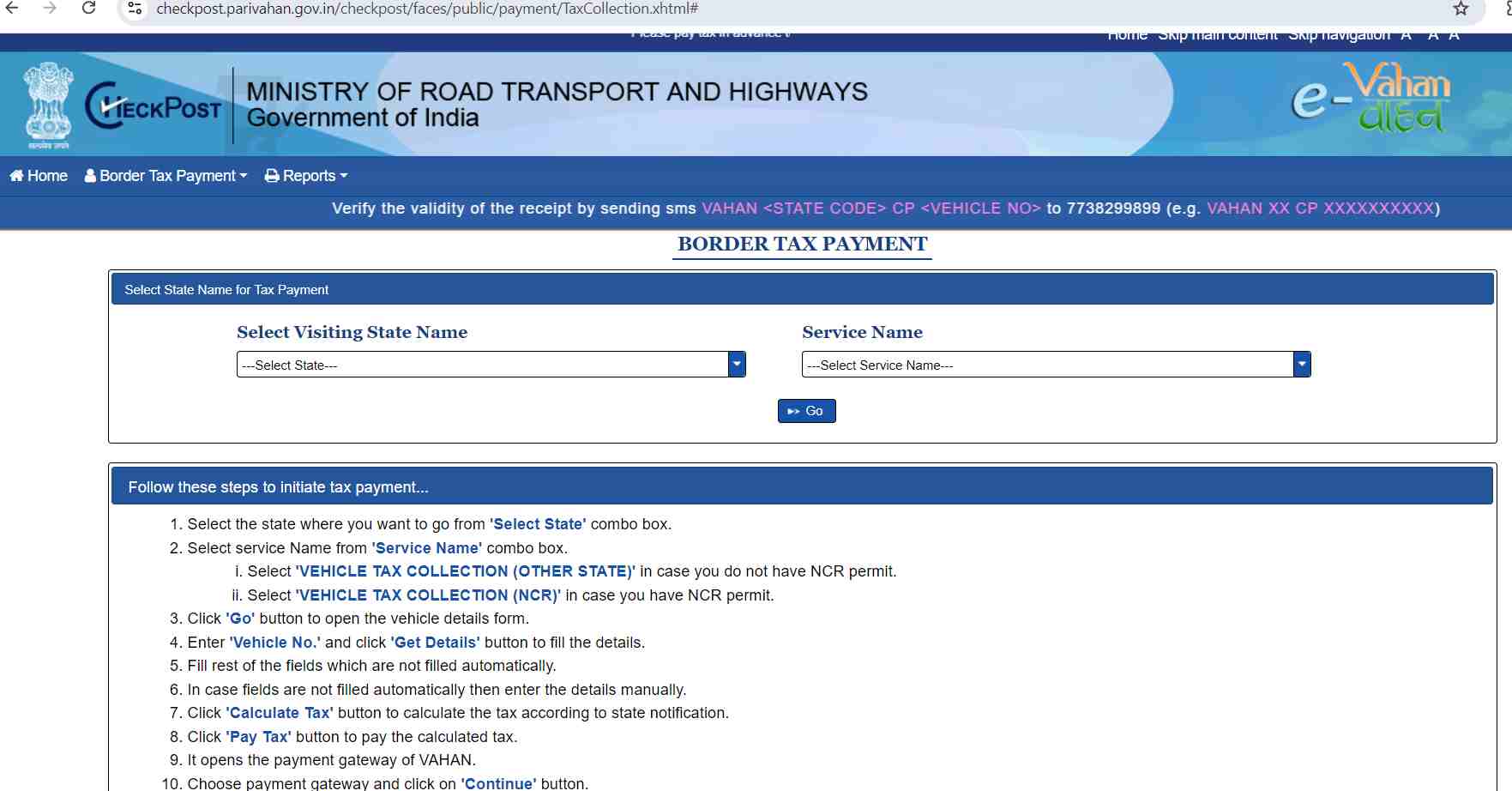
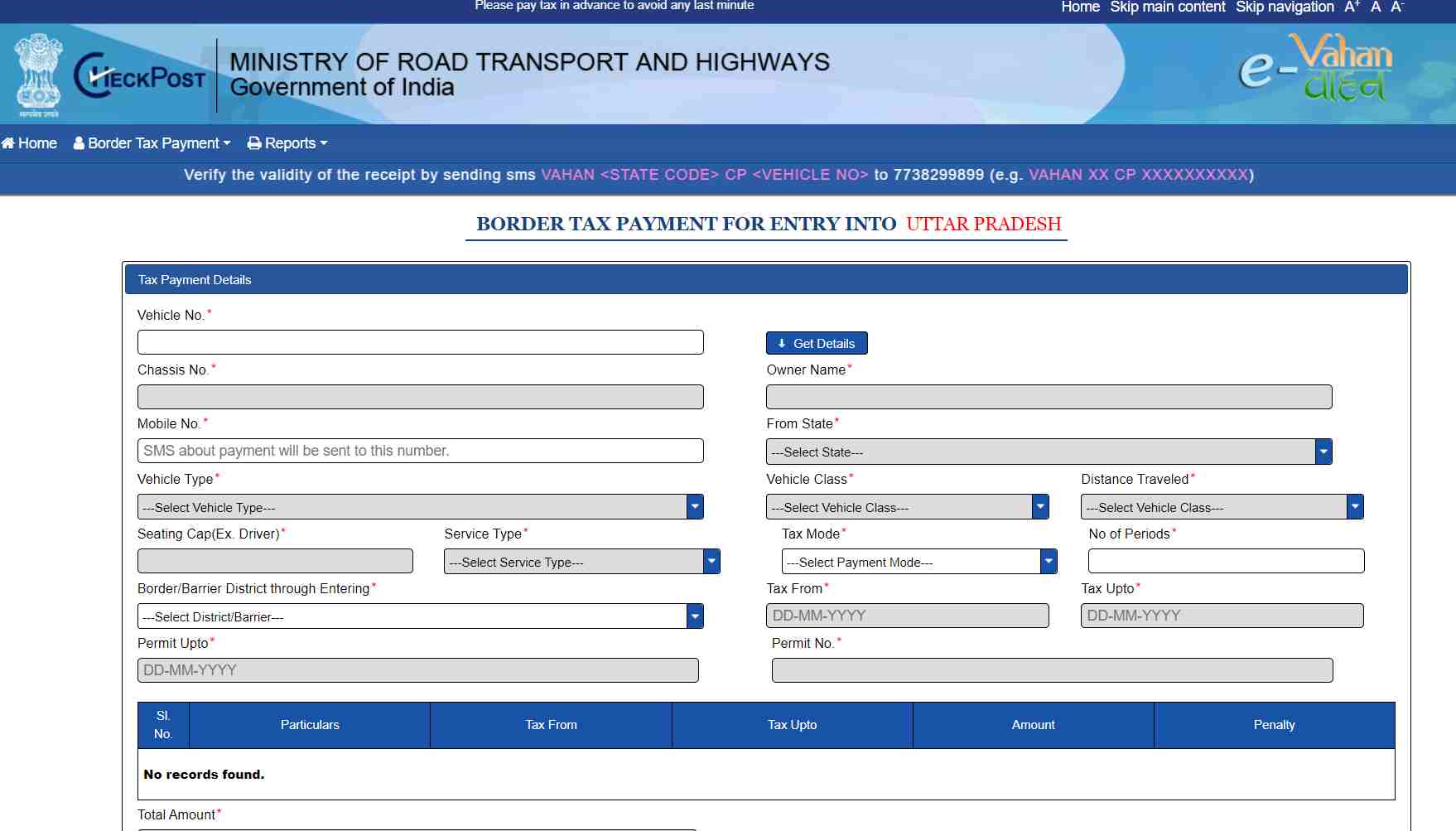
To pay road tax online in Maharashtra, follow the steps listed below:
Step 1: Go to the official e-Vahan portal and click on the ‘Tax Payment’ option.

Penalty for Not Paying Road Tax in Maharashtra
In Maharashtra, you are liable to pay the road tax within 30 days of registering your vehicle. In case you fail to do so, you are liable to pay a penalty.
For first-time offenders, the fine amount ranges from ₹300 to the one-time tax amount for that vehicle category. However, for repeat offenders, the penalty may rise to twice the amount of the one-time payable tax.
List of RTOs in Maharashtra
Here is a list of RTOs where you can pay road tax in Maharashtra:
| RTO Code | RTO Location |
| MH-01 | Tardeo |
| MH-02 | Andheri |
| MH-03 | Worli Deputy |
| MH-03 | Wadala |
| MH-04 | Thane - Central Mumbai |
| MH-05 | Kalyan |
| MH-06 | Raigad |
| MH-07 | Sindhudurg |
| MH-08 | Ratnagiri |
| MH-09 | Kolhapur |
| MH-10 | Sangli |
| MH-11 | Satara |
| MH-12 | Pune |
| MH-13 | Solapur |
| MH-14 | Pimpri Chinchwad |
| MH-15 | Nashik |
| MH-16 | Ahmednagar |
| MH-17 | Shrirampur |
| MH-18 | Dhule |
| MH-19 | Jalgaon |
| MH-20 | Aurangabad |
| MH-21 | Jalna |
| MH-22 | Parbhani |
| MH-23 | Beed |
| MH-24 | Latur |
| MH-25 | Osmanabad |
| MH-26 | Nanded |
| MH-27 | Amravati |
| MH-28 | Buldhana |
| MH-29 | Yavatmal |
| MH-30 | Akola |
| MH-31 | Nagpur |
| MH-33 | Gadchiroli |
| MH-34 | Chandrapur |
| MH-35 | Gondia |
| MH-36 | Bhandara |
| MH-37 | Washim |
| MH-38 | Hingoli |
| MH-39 | Nandurbar |
| MH-40 | Wadi Nagpur |
| MH-41 | Malegaon |
| MH-42 | Baramati |
| MH-43 | Vashi Deputy |
| MH-44 | Ambejogai Beed |
| MH-45 | Akluj |
| MH-46 | Panvel Deputy |
| MH-47 | Dahisar Deputy |
| MH-48 | Vasai |
| MH-49 | Nagpur (East) |
| MH-50 | Karad |
| MH-51 | Sangamner |
| MH-52 | Parbhani (Rural) |
| MH-53 | Pune South |
| MH-54 | Pune North |
| MH-55 | Mumbai Central |
| MH-56 | Thane Rural |
Timely paying road tax in Maharashtra is essential whenever you buy a new vehicle or renew the registration of your existing automobile. Otherwise, it can attract hefty penalties, which can get significantly higher in case you keep delaying.
So, if your vehicle’s road tax is due, you can easily pay it online by following the steps mentioned above or by visiting your nearest RTO. This way, you will not only be keeping legal hassles at bay but also contributing to the Government’s maintenance.
















