I agree to the Terms & Conditions


General
General Products
Simple & Transparent! Policies that match all your insurance needs.


4.7
Rated App56K+ Reviews
4.3
Rated App11K+ Reviews
Scan to download
Life
Life Products
Digit Life is here! To help you save & secure your loved ones' future in the most simplified way.


4.7
Rated App56K+ Reviews
4.3
Rated App11K+ Reviews
Scan to download
Claims
Claims
We'll be there! Whenever and however you'll need us.


4.7
Rated App56K+ Reviews
4.3
Rated App11K+ Reviews
Scan to download
Resources
Resources
All the more reasons to feel the Digit simplicity in your life!
 Tools & Calculators
Tools & Calculators


4.7
Rated App56K+ Reviews
4.3
Rated App11K+ Reviews
Scan to download
4.7
Rated App56K+ Reviews
4.3
Rated App11K+ Reviews
 Logout
Logout
Our WhatsApp number cannot be used for calls. This is a chat only number.


2000+ Cashless
Network Garages
96% Claim
Settlement (FY23-24)
24*7 Claims
Support
I agree to the Terms & Conditions

Terms and conditions
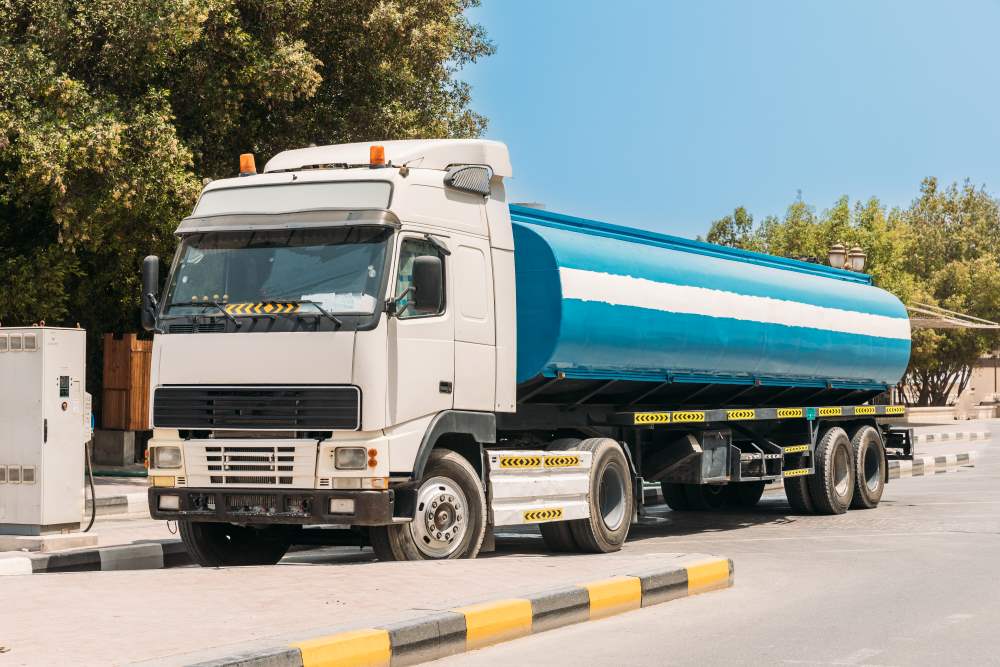

Tank trucks, also known as tank transport trucks, large tanker trucks, or tank carrier trucks, are an indispensable part of the logistics and transportation industry.
These specialised vehicles are pivotal in transporting various types of liquid cargo, ranging from chemicals to food products, across vast distances.
In this comprehensive article, we will explore the world of tank trucks, examining their various types, dimensions, benefits and common uses.
A tank truck is a motor vehicle designed to carry liquids or gases in a container known as a tank. The design of a tank truck ensures that the cargo remains stable and secure during transit, even when the vehicle is in motion.
Tank trucks are common on highways and roadways, showcasing their versatility in transporting a wide range of materials.

Tank trucks come in various configurations, each tailored to the specific needs of the cargo they transport. Below, we will delve into seven types of tank trucks:

Insulated tankers are equipped with a layer of insulation to maintain the temperature of the cargo. They transport temperature-sensitive liquids, such as chemicals or food products, that require precise temperature. Insulated tankers are typically available in various sizes, with capacities ranging from 3000 - 11,000 gallons.

Food-grade tankers are specifically designed to transport food products, such as milk, fruit juices, and edible oils, ensuring the cargo remains uncontaminated and safe for consumption. Food-grade tankers come in sizes, from 2,000 to 8,000 gallons.
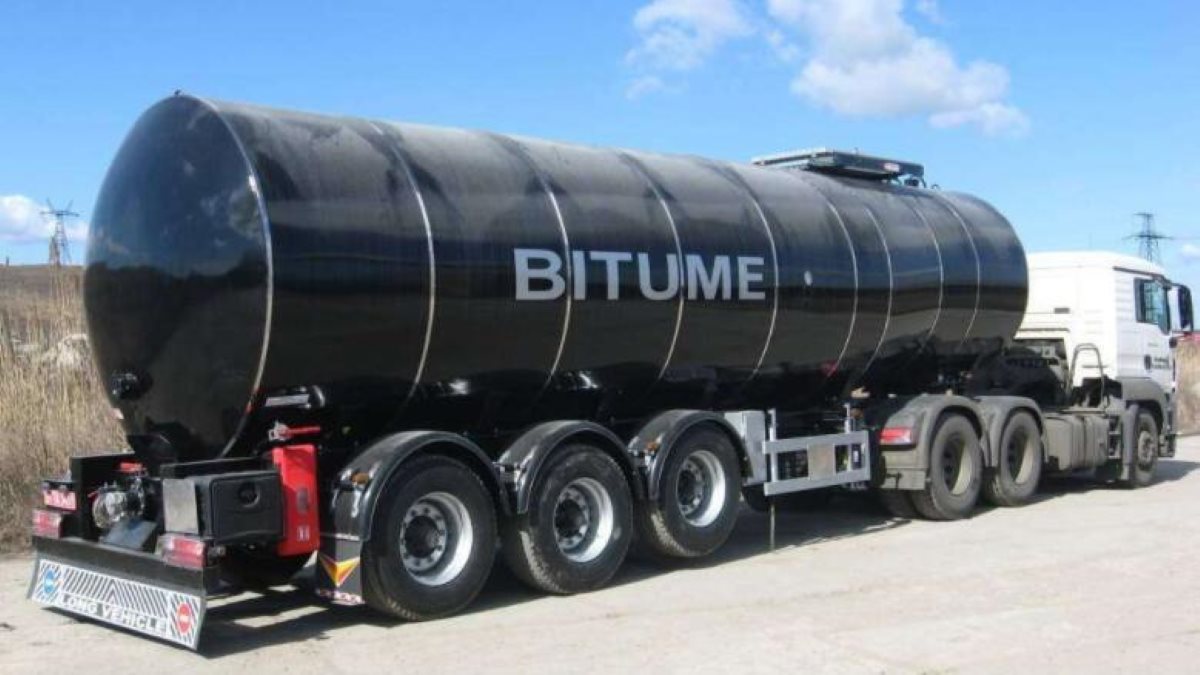

Asphalt tankers are constructed with special materials and insulation to handle the high temperatures required for transporting hot asphalt.
These tankers are employed in the construction industry to transport hot asphalt for road paving, roofing materials, and other applications. Asphalt tankers typically have a capacity of 5,000 to 7,000 gallons.
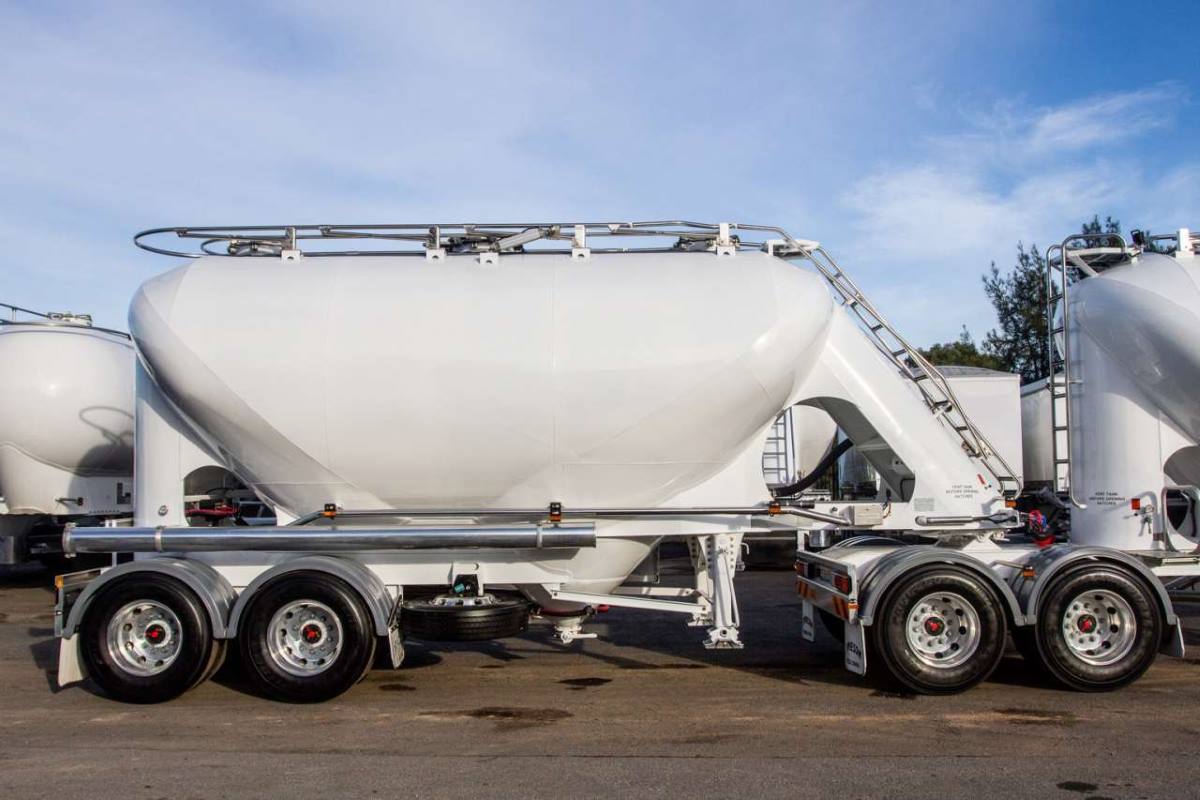

Pneumatic tankers are designed to transport dry bulk materials such as cement, sand, and powdered chemicals. They use compressed air to unload their cargo. They can vary in size, but their capacity typically ranges from 500 to 3120 cubic feet.
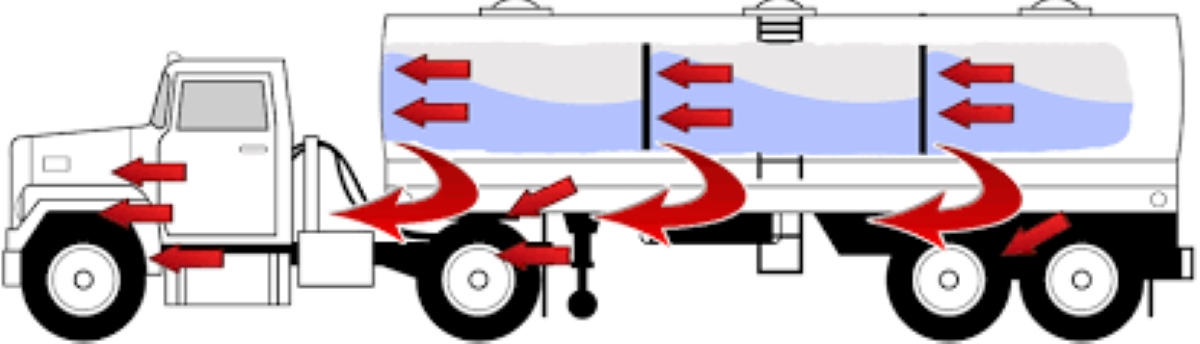
Bulkhead tankers have internal bulkheads that create compartments within the tank, allowing for transporting multiple types of cargo simultaneously.
These partitions inside the tank prevent the cargo from sloshing during transportation, ensuring stability. Bulkhead tankers come in sizes ranging from 6,000 to 11,000 gallons.
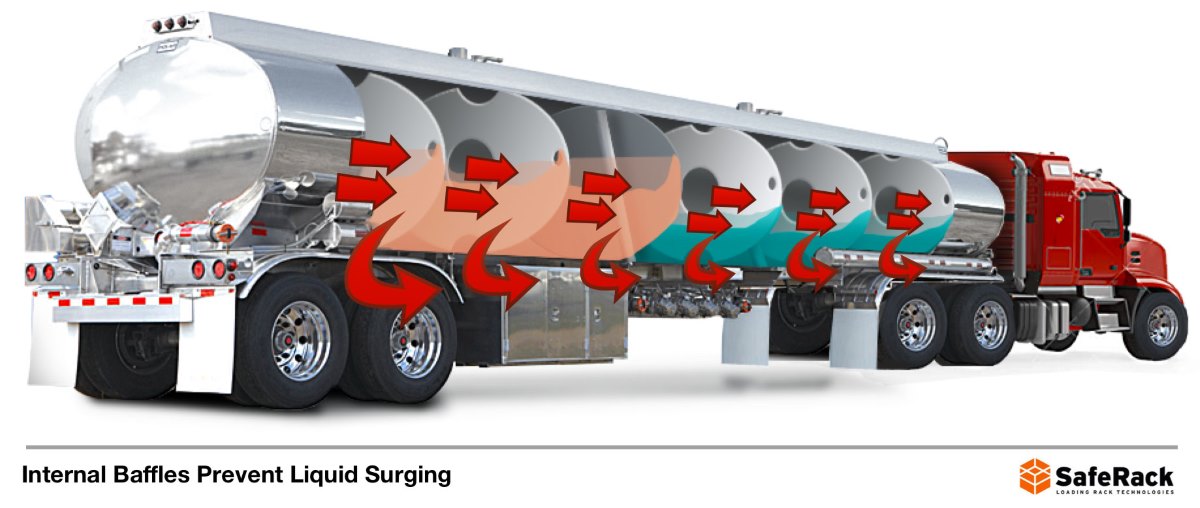
Baffle tankers have built-in baffles or partitions inside the tank, which reduce the sloshing of liquids during transit, enhancing stability and safety.
Baffles are angled partitions with holes that reduce the front-to-back movement of the liquid cargo transported by the tanker. Baffle tankers can vary in size, with capacities from 3,000 to 11 600 gallons.
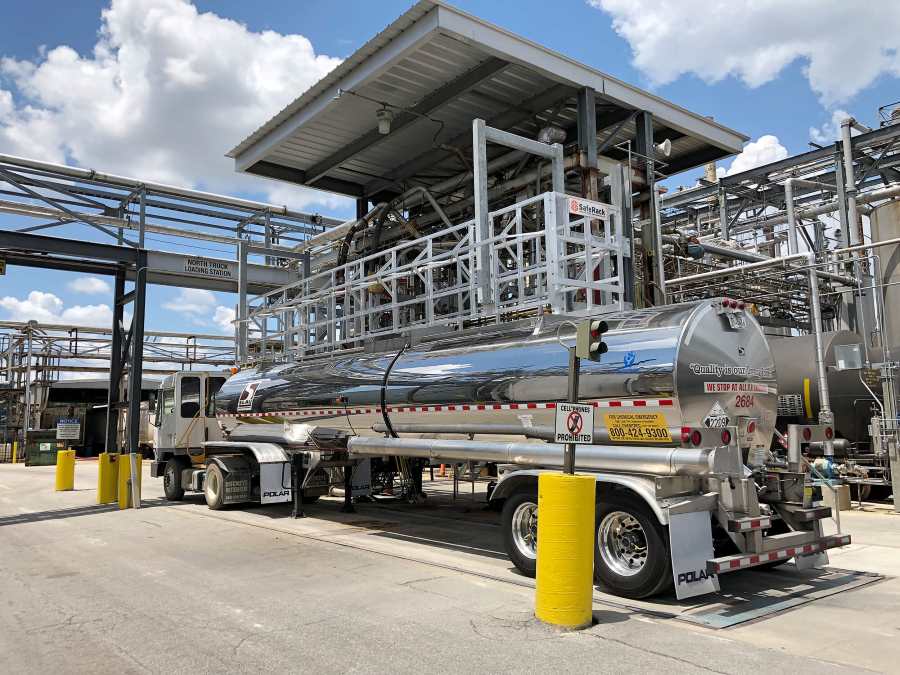

Smoothbore tankers have a smooth interior surface that facilitates the easy cleaning and unloading of various liquid cargo, making them versatile for various materials.
It makes them ideal for transporting chemicals and other liquids that may be corrosive or reactive. Smoothbore tankers come in sizes ranging from 5,500 to 11,600 gallons.
Tank trucks offer several advantages, making them an essential part of the transportation industry:
Tank trucks serve numerous industries and fulfil a variety of transportation needs. Some common uses include:
Therefore, tank trucks are the workhorses of liquid cargo transportation, offering a wide range of configurations to meet the diverse needs of industries worldwide. From food-grade tankers to asphalt carriers, these specialised vehicles play a pivotal role in ensuring the safe and efficient movement of liquids, making them an indispensable part of the global supply chain.
The area(A) of the round end is multiplied by the height H to determine the total capacity of a cylindrical water tank.
The area(A) of the round end is multiplied by the height H to determine the total capacity of a cylindrical water tank.
The average capacity of an Indian tank truck is 20000 to 30000 litres.
The average capacity of an Indian tank truck is 20000 to 30000 litres.
The maximum capacity of small tanker trucks is 3,000 gallons, while the maximum capacity of large tankers is 11,600 gallons.
The maximum capacity of small tanker trucks is 3,000 gallons, while the maximum capacity of large tankers is 11,600 gallons.
In 1905, the first contemporary tank vehicles were created, and by 1910, urban areas were filled with them. While still using horses, rural areas began to use tank trucks around 1920.
In 1905, the first contemporary tank vehicles were created, and by 1910, urban areas were filled with them. While still using horses, rural areas began to use tank trucks around 1920.
Please try one more time!
Other Important Articles About Truck
Other Important Articles about Commercial Vehicle Insurance
Have queries related to Digit motor insurance policy? You can refer to our Policy Wordings for detailed information or reach out to our support team via WhatsApp self-support, email or phone using the information below:
Connect with our self-serve chat bot support - 7026061234
Write to us at hello@godigit.com
Contact
Call us on 1800-258-5956
Other Motor Insurance Plans and Guides
Currently there are no news to show.
20-02-2025
Electric Buses In India: ICRA Predicts Big Growth by FY30
The credit rating agency ICRA estimates that electric three-wheelers (e3Ws) will dominate electric vehicle penetration, reaching 40% by FY30. The Indian government supports this transition with schemes like PM e-Bus Sewa. By 2030, electric buses and light commercial vehicles will also see significant growth. Government subsidies, lower costs, and technological advancements will drive this shift. The automotive component sector is expected to invest heavily in capacity expansion and localization to support this electrification trend
08-02-2025
Tractor Segment to Grow Over 15% in Q4; Decline in Other CVs
Mahindra & Mahindra forecasts over 15% growth in the tractor segment for Q4, driven by good reservoir levels, favourable rabi sowing, and strong kharif production. Tractor sales reached 8.94 lakh units in CY2024, marking a 2.55% growth compared to the previous year, as per FADA. However, the commercial vehicle segment remains weak, with recovery expected next fiscal year.
27-01-2025
Auto Exports Hit 19% Rise in 2024; Driven by Robust Demand Revival in EMs
Strong demand from emerging markets, like Latin America and Africa, led to a 19% increase in India's automobile exports in 2024, which was driven by two-wheelers, passenger vehicles, and commercial vehicles. The overall shipments rose to 50,98,810 units from 42,85,809 units exported in 2023, as per SIAM data. However, the export of passenger cars fell by 4%.
Read More
Renew & Download Policy Document, Check Challan, Credit Score, PUC & more
Anytime, Anywhere. Only on Digit App!

4.7
Rated App56K+ Reviews
4.7
Rated App
56K+ Reviews
4.3
Rated App11K+ Reviews
4.3
Rated App
11K+ Reviews
Scan to Download


Author: Team Digit
Last updated: 25-04-2025
CIN: L66010PN2016PLC167410, IRDAI Reg. No. 158.
Go Digit General Insurance Limited | Corporate Office Address: Atlantis, 95, 4th B Cross Road, Koramangala Industrial Layout, 5th Block, Bengaluru 560095 | Registered Office Address: 1 to 6 floors, Ananta One (AR One), Pride Hotel Lane, Narveer Tanaji Wadi, Shivaji Nagar, Pune-411005, Maharashtra | Trade logo of Go Digit General Insurance Ltd. displayed above belongs to Go Digit lnfoworks Services Private Limited and is provided and used by Go Digit General Insurance Ltd. under license.
Explore exclusive features, file claims & access policy on Digit App!
You can also scan this QR code to download the App.

