2000+ Cashless Garages
60 Lakh+ Policies Sold

2000+ Cashless Garages
60 Lakh+ Policies Sold

In India, where the logistics and transportation sector is a cornerstone of the economy, trucks come in a wide range of sizes and configurations to meet the diverse needs of the industries.
Understanding the different sizes and types of trucks available is essential for anyone involved in distribution or transportation planning. In addition, it's essential to think about purchasing a truck insurance policy, which will protect the machinery in the event of an accident.
In this article, we will delve into the world of truck sizes in India, exploring their importance, common uses, services provided, specific functions, and geographical areas of operation, and providing examples to illustrate each type.
Trucks come in various sizes to cater to different transportation needs. Here is a list of 7 different types of trucks based on their size and usage:

EHCVs can carry larger payloads in a single trip, reducing the need for multiple shipments and lowering transportation costs. This results in lower fuel consumption and emissions, contributing to environmental sustainability.
Key Details:

Their weight distribution design helps protect road infrastructure and enhance road safety. Efficient cargo transport leads to cost savings for businesses, as it reduces the need for multiple trips.
Key Details:

Container trucks are efficient in the handling of containers to ensure timely delivery and minimise cargo handling at various points in the supply chain. Their standardised design ensures smooth and efficient cargo handling.
Key Details:
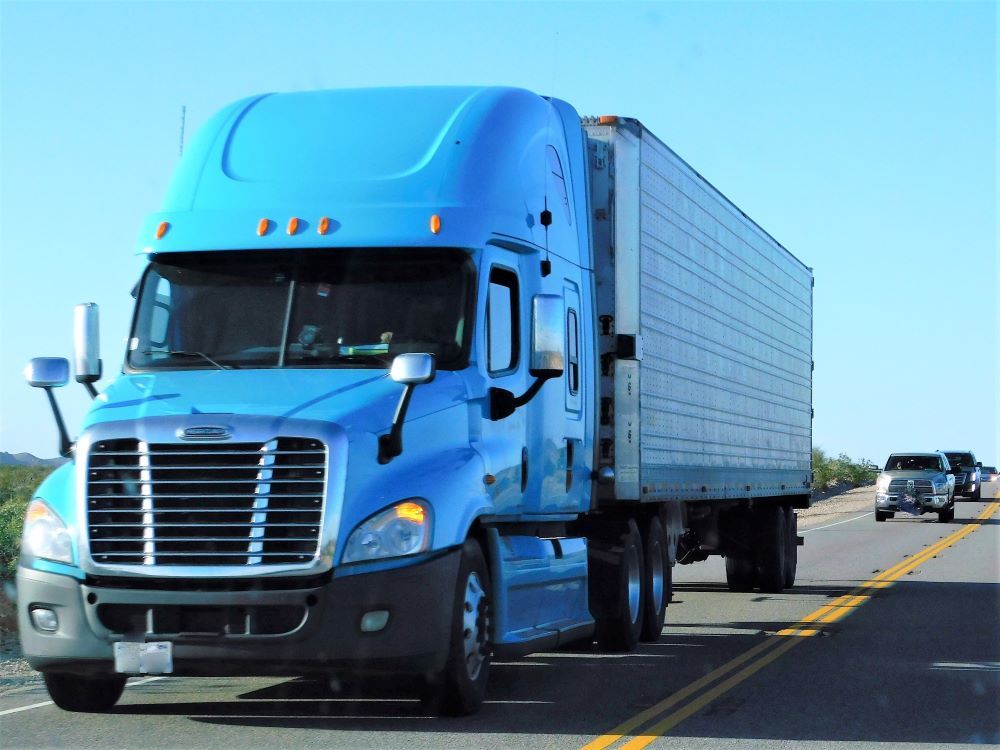

HCVs offer cost-effective transportation for bulk goods due to their ability to carry large quantities in a single trip. They are known for their reliability in challenging conditions, ensuring goods reach their destinations on time
Key Details:
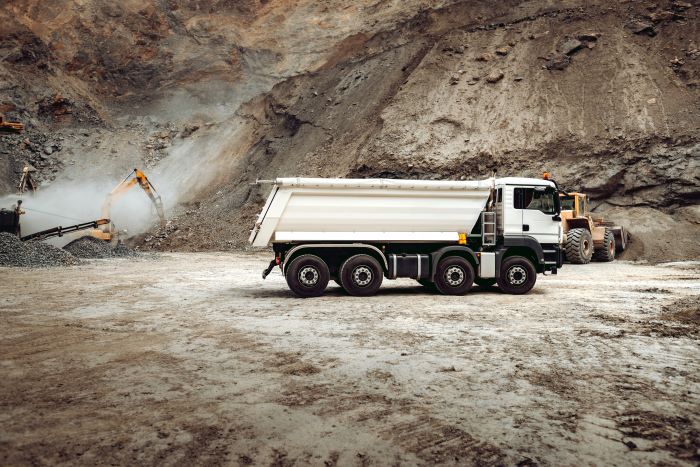

Their flexibility in handling medium loads makes them adaptable to diverse transportation needs. MCVs are designed with fuel-efficient engines, helping businesses reduce their operating costs and environmental impact.
Key Details:

Light commercial vehicles come in a compact size that allows them to access narrow lanes and congested areas, reducing the need for multiple handling of goods.
Key Details:
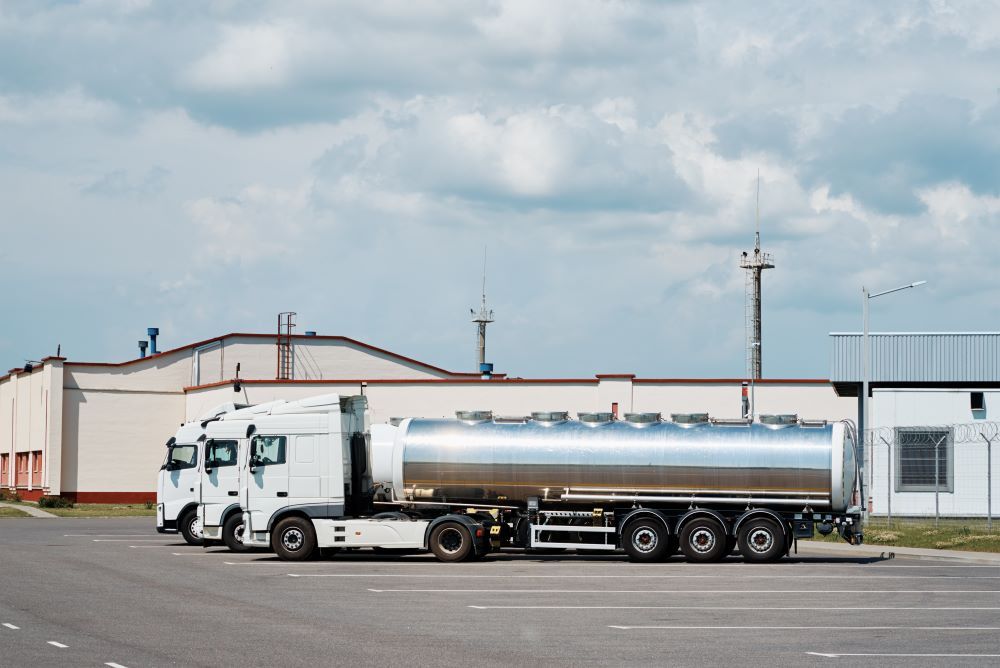

Goods can be loaded onto a trailer at the point of origin and unloaded at the destination, reducing the need for multiple handling processes. They are equipped with safety features, such as brakes and lighting.
Key Details: