What Is Sonography Test: Types, Procedure, Precautions, & More
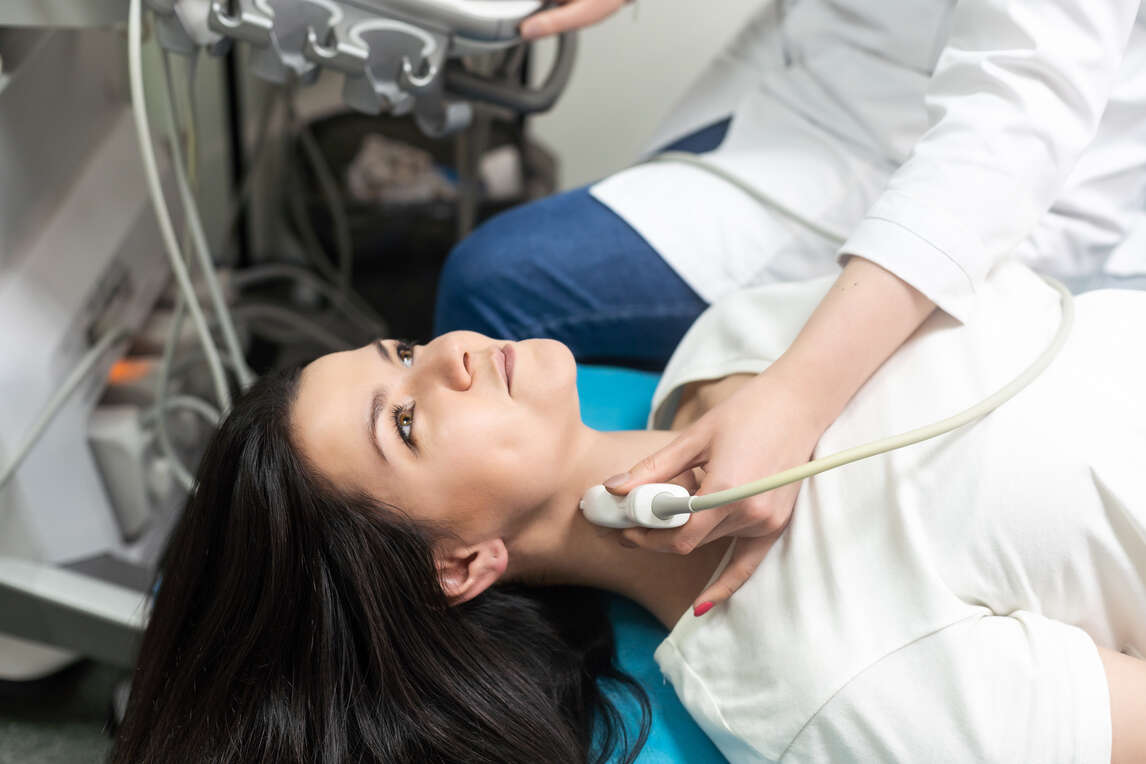
Sonography, commonly known as ultrasound, is more than checking foetal growth during pregnancy. It helps doctors identify underlying issues with your vessels, tissues, and organs without requiring an incision.
This article will explain all about what sonography is, the types, precautions, and risks associated with the same. Read on to know more!
What Is Sonography?
An ultrasound or sonography is a safe and non-invasive clinical examination method that uses high-frequency sound waves to record images inside your body. For instance, sonography effectively monitors the progress in pregnancy in obstetrics and assists in identifying heart function and physiology in cardiology.
It also visualises tumours and how they respond during treatments in oncology. In addition, unlike other imaging methods, sonography includes no ionising radiation.
What Are the 11 Different Types of Sonographies?
Besides knowing what sonography is, you must understand that there are various techniques to diagnose different body conditions. Here are the different types of sonographies and their uses for each:
1. Hysterosonography
Much like a gynecologic exam, the sonohysterography or hysterosonography method uses sound waves to capture images inside a woman’s uterus.
Uses of Hysterosonography: It helps to diagnose miscarriages, infertility, and unexplained vaginal bleeding.
2. Obstetric Ultrasound
This sonography test uses sound waves to capture images of an embryo or a foetus in a pregnant woman.
Uses of Obstetric Ultrasound: It is considered a preferred method to monitor pregnancy and the child's development inside a mother’s womb.
3. Abdomen Ultrasound
This method captures images of the structures in your upper abdomen.
Uses of Abdomen Ultrasound: It assists in diagnosing abdominal pain or enlargement and examines the functioning of kidneys, gallbladder, liver, pancreas, spleen, bile ducts, and aorta.
4. Breast Ultrasound
In this method, the sound waves capture pictures of the internal structures of a breast.
Uses of Breast Ultrasound: Doctors conduct this method to diagnose breast lumps and other abnormal structures found while performing a breast MRI or a mammogram.
5. Carotid Ultrasound
Carotid sonography uses sound waves to capture images of the carotid arteries in your neck. This artery carries blood from your heart to your brain. Besides, doppler technology is also part of this exam.
Uses of Carotid Ultrasound: This method is used to diagnose narrowing or blockage of carotid arteries (stenosis) that increases the chances of stroke.
6. Musculoskeletal Ultrasound
This method captures images of your body's muscles, ligaments, nerves, tendons, and joints.
Uses of Musculoskeletal Ultrasound: It helps to diagnose strains, arthritis, sprains, tears, trapped nerves, and related musculoskeletal conditions in a body.
7. Pelvic Ultrasound
Pelvic sonography captures pictures of the organ structure in your pelvis and lower abdomen. Moreover, there are three different types of pelvic sonography which include- vaginal (for women), abdominal, and rectal (for men).
Uses of Pelvic Ultrasound: Doctors use this method to diagnose issues in your body's urinary and reproductive systems.
8. Prostate Ultrasound
This method produces images of the prostate gland.
Uses of Prostate Ultrasound: It assists in diagnosing difficulty while urinating. Additionally, this method helps to detect a nodule found during a rectal exam, an enlarged gland, abnormal structures, or an elevated blood test result.
9. Scrotum Ultrasound
This method uses sound waves to capture images of the testicles and the surrounding tissues of a male.
Uses of Scrotum Ultrasound: It is a primary procedure that allows the evaluation of testicle disorder, epididymis, or the tubes precisely next to the testicles and scrotum.
10. Thyroid Ultrasound
This method uses sound waves to capture images of the thyroid gland in your neck.
Uses of Thyroid Ultrasound: Doctors conduct this method to examine nodules or lumps while evaluating a routine physical exam or related imaging test.
11. Venous Ultrasound
This method uses sound waves to capture pictures of the veins in your body.
Uses of Venous Ultrasound: It commonly helps to diagnose blood clots, especially in the veins of your leg. Also, it examines deep vein thrombosis effectively.
How Does Sonography Work?
It is essential to learn the way it works to know about sonography tests thoroughly:
Step 1: In sonography, an instrument known as a transducer releases high-frequency inaudible sound waves.
Step 2: These sound waves travel steadily inside your body until they hit a dense object such as a bone or an organ.
Step 3: Then, depending on the tissue present, these waves either continue to travel further or get reflected.
Step 4: The sound waves that reflect or echo get communicated to the ultrasound device.
Step 5: Depending on the return time of each echo and the speed of sound waves in tissues, the imaging device calculates the distance. It is between every structure and the probe.
Step 6: The intensity and distance of all echoes are modified into a 2-dimensional image. This appears on the sonography imaging screen.
Sonographers and ultrasound specialists are well-versed in performing this test, after which a doctor or a radiologist interprets the images.
How to Prepare for a Sonography?
Every medical test and examination come with its own set of rules that both you and your doctor follow. However, depending on the doctor's suggestion, below are the things you must follow to prepare for the test:
- Always carry out the instructions provided by the doctor carefully. For instance, in a gallbladder ultrasound test, your medical practitioner might ask you to eat or drink for a specific period before the test. While for a pelvic ultrasound, you might require a full bladder. In that case, prevent urinating till the test is done.
- It is necessary to wear loose or comfortable clothing during your ultrasound test. Besides, do not wear any jewellery during the test. This helps the ultrasound specialist easily access the body area required for screening.
- Since different ultrasound tests require different needs, confirm with your doctor if you can undergo this test consuming your medicines or supplements (if any) or without.
- Do not panic before or during the examination since it is an entirely non-invasive test that doesn't require any incision.
What Is the Procedure for Sonography?
The procedure for sonography is simple and continues for only a few minutes. Here is the process of the test:
Procedure Before the Sonography Test:
Step 1: Before the sonography exam, your doctor will ask you to remove any jewellery you wear to examine.
Step 2: Next, you will have to change into a gown so they can examine the area easily.
Step 3: The staff will ask you to lie on an examination table.
Step 4: Lastly, to start the process, your sonographer might cut or remove some of the clothing from the examination area.
Procedure During the Sonography Test:
Step 5: A sonographer will apply a lubricating gel over the examination area to prevent air pockets from blocking sound waves that create images. This gel is easy to remove and doesn’t cause side effects.
Step 6: A sonographer will press a transducer against the examination area and move it as required to capture pictures of that area.
Step 7: The device sends sound waves in your body and gathers the ones that reflect. This, when sent to the computer, creates pictures.
Step 8: In some instances, doctors conduct an ultrasound inside your body by attaching a transducer to the probe and inserting it into a natural opening in your body.
Step 9: After the procedure, the sonographer cleans off the gel on your skin, and you can resume your normal activities.
Procedure Post the Sonography Test:
Step 10: After conducting sonography, your medical expert will review all the images captured during the process and detect any abnormalities in your body.
Step 11: They might discuss reports and findings with you. Furthermore, you might need to undergo a CT scan, an MRI, or a biopsy tissue sample if there are any abnormalities.
Step 12: After your doctor diagnoses your condition based on these reports, they will start your treatment accordingly.
During the process, you might be required to change positions as per the technician’s instructions so that they can have better access to the examination area. This whole procedure lasts for 30 minutes or less than that, depending entirely on the area of examination and the type of ultrasound done.
It is important to note that during a Transesophageal Echocardiogram, the professional may insert a transducer inside your oesophagus. It is to collect images of your heart. Moreover, this process usually takes place under sedation. During the Transrectal method, a technician places a transducer inside the rectum. Additionally, in the transvaginal procedure, it goes inside a vagina.
What Are the Risk Factors in Sonography?
Sonography, generally, doesn't include any risk, adverse effects, or complications. Moreover, since it is devoid of radiation, you also have no fear of side effects.
However, there might be few chances of raising the temperature of surrounding tissues in the examination area. Also, you must only undergo this test under the guidance of a trained practitioner.
What Are the Benefits of Sonography?
Ultrasonography ensures a better and more detailed view of the functioning of organs, muscles, bones, etc. The benefits of sonography include the following:
- Painless: Ultrasonography is painless and doesn't include injections, needles, or incisions.
- Provides Internal Image: This method effectively captures pictures of the soft tissues that generally don't appear in standard X-ray tests.
- No Radiation Exposure: You are never exposed to ionising radiation and do not have any fear of any harmful side effects.
- Good Alternative: It is an excellent alternative to MRI if you are claustrophobic.
- Accessible: This method is widely accessible and less expensive than other methods.
What Are the Precautions to Take in Sonography?
Following are the precautions both you and a sonographer require to maintain:
- Take Professional Assistance: An ultrasound device must be calibrated by well-versed personnel to ensure the ultrasonic power is within the set parameters.
- Do Not Touch Face: A sonographer must not touch the applicator’s face when the device is in operation.
- Avoid Thermal Damage: An operator must turn on this device after rubbing the lubricator to avoid thermal damage to the system.
- Wear a Dry and Soft Glove: To prevent scattered ultrasound from entering a sonographer’s hand during underwater treatment, they must wear a dry and soft glove inside a rubber one to ensure air gap protection.
- Ensure Minimum Patient Exposure: Your sonographer must use minimum patient exposure to prevent health effects from getting the required results.
- Use Coupling Media: As ultrasound reflects at an air tissue interface, a sonographer must use a coupling media between you and the applicator area to avoid any damage or bruise on your body.
- Keep the Transducer Moving: A sonographer must keep moving the transducer at an angle of 90 degrees on the treatment surface to reduce the risk of causing hot spots, arresting blood flow, and damage to blood vessel walls.
- Do Not Apply on Sensitive Area: Sonography must not take place in areas with significantly less pain or heat sensitivity.
- Avoid Exposure to Foetus: If you are pregnant, a sonographer must be careful and not use this method on any other body area exposed to the foetus.
- Be Careful of the Area of Application: The sonographer must not use ultrasound on your eye, an area with diminished blood circulation, large peripheral nerves and vertebral column, or any anaesthetic area.
- Inform About Cardiac Pacemaker: You must let your doctor know if you have a cardiac pacemaker, as ultrasound cannot be used in your thoracic area in this case.
So, now you know what is sonography and its benefits, and the easy process it includes. First, however, ensure only a skilled professional is conducting this process, delivering prescribed doses, maintaining all safety measures and adhering to guidelines.
Protect What Matters - Explore Other Insurance Options














